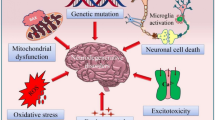
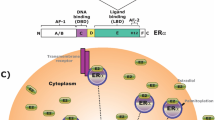
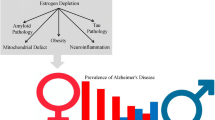
Abstract
Epidemiologic studies revealed that the prevalence of Parkinson disease is higher in males than in females and that the progression of the disease might be rapid in males compared with females. The reason for the gender difference is unknown; however, estrogens may be involved. Many studies have revealed that estrogens provide neuroprotective effects and that the protective mechanisms include antioxidant property and upregulation of Bcl-2, brain-derived neurotrophic factor, and glial cell-derived neurotrophic factor (GDNF). Upregulation of Bcl-2 or GDNF is mediated by nonnuclear estrogen receptor (ER) in addition to transcription regulation by ER. To avoid undesirable effect of estrogens, several selective ER modulators, raloxifene and genistein are considered.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nurmi, E., Ruottinen, H. M., Kaasinen, V., et al. (2000). Ann. Neurol. 47, 804–808.
Pirker, W., Djamshidian, S., Asenbaum, S., et al. (2001). Mov. Disord. 17, 45–53.
Bauer, R. B., Stevens, C., Reveno, W. S., and Rosenbaum, H. (1982). J. Am. Geriatr. Soc. 30, 322–325.
Li, S. C., Schoenberg, B. S., Wang, C. C., et al. (1985). Arch. Neurol. 42, 655–657.
Jankovic, J. and Kapadia, A. S. (2001). Arch. Neurol. 58, 1611–1615.
Leranth, C., Roth, R. H., Elswoth, J. D., Naftolin, F., Horvath, T. L., and Redmond, J. D. E. (2000). J. Neurosci. 20, 8604–8609.
Mooradian, A. D. (1993). J. Steroid Biochem. Mol. Biol. 45, 509–511.
Negre Salvayre, A., Pieraggi, M. T., Mabile, L., and Salvayre, R. (1993). Atherosclerosis 99, 207–217.
Rifici, V. A. and Khachadurian, A. K. (1992). Metabolism 41, 1110–1114.
Keller, J. N., Germeyer, A., Begley, J. G., and Mattson, M. P. (1997). J. Neurosci. Res. 50, 522–530.
Behl, C., Skutella, T., Lezoualc’h, F., et al. (1997). Mol. Pharmacol. 51, 535–541.
Sawada, H., Ibi, M., Kihara, T., Urushitani, M., Akaike, A., and Shimohama, S. (1998). J. Neurosci. Res. 54, 707–719.
Gridley, K. E., Green, P. S., and Simpkins, J. W. (1998). Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 874–880.
Ambani, L. M., Van Woert, M. H., and Murphy, S. (1975). Arch. Neurol. 32, 114–118.
Perillo, B., Sasso, A., Abbondanza, C., and Palumbo, G. (2000). Mol. Cell. Biol. 20, 2890–2901.
Honda, K., Sawada, H., Kihara, T., et al. (2000). J. Neurosci. Res. 60, 321–327.
Honda, K., Shimohama, S., Sawada, H., et al. (2001). J. Neurosci. Res. 64, 466–475.
Lee, S. J. and McEwen, B. S. (2001). Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 41, 569–591.
Simpkins, J. W., Green, P. S., Gridley, K. E., Singh, M., de Fiebre, N. C., and Rajakumar, G. (1997). Am. J. Med. 103, 19S-25S.
Ivanova, T., Karolczak, M., and Beyer, C. (2002). Endocrinology 143, 3175–3178.
Xie, T., Ho, S. L., and Ramsden, D. (1999). Mol. Pharmacol. 56, 31–38.
Tsang, K. L., Ho, S. L., and Lo, S. K. (2000). Neurology 54, 2292–2298.
Burns, R. S., Chiueh, C. C., Markey, S. P., Ebert, M. H., Jacobowitz, D. M., and Kopin, I. J. (1983). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 80, 4546–4550.
Langston, J. W., Ballard, P., Tetrud, J. W., and Irwin, I. (1983). Science 219, 979–980.
Naoi, M., Maruyama, W., Dostert, P., and Hashizume, Y. (1997). J. Neural Transm. 50(Suppl.), 89–105.
Maruyama, W., Strolin-Benedetti, M., and Naoi, M. (2000). Neurobiology 8, 55–68.
Ramsay, R. R., Salach, J. I., and Singer, T. P. (1986). Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 134, 743–748.
Mizuno, Y., Sone, N., and Saitoh, T. (1987). J. Neurochem. 48, 1787–1793.
Gelinas, S. and Martinoli, M. G. (2002). J. Neurosci. Res. 70, 90–96.
Sawada, H., Ibi, M., Kihara, T., et al. (2002). Neuropharmacology 42, 1056–1064.
Callier, S., Le Saux, M., Lhiaubet, A. M., Di Paolo, T., Rostene, W., and Pelaprat, D. (2002). J. Neurochem. 80, 307–316.
Grandbois, M., Morissette, M., Callier, S., and Di Paolo, T. (2000). Neuroreport 11, 343–346.
Kuiper, G. G., Enmark, E., Pelto-Huikko, M., Nilsson, S., and Gustafsson, J. A. (1996). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 93, 5925–5930.
Shughrue, P. J., Lane, M. V., and Merchenthaler, I. (1997). J. Comp. Neurol. 388, 507–525.
Kuiper, G. G., Carlsson, B., Grandien, K., et al. (1997). Endocrinology 138, 863–870.
Barkhem, T., Carlsson, B., Nilsson, Y., Enmark, E., Gustafsson, J., and Nilsson, S. (1998). Mol. Pharmacol. 54, 105–112.
Paech, K., Webb, P., Kuiper, G. G., et al. (1997). Science 277, 1508–1510.
Qiu, Y., Waters, C. E., Lewis, A. E., Langman, M. J., and Eggo, M. C. (2002). J. Endocrinol. 174, 369–377.
Kim, H. T., Kim, B. C., Kim, I. Y., et al. (2002). J. Biol. Chem. 277, 32510–32515.
Sawada, H., Ibi, M., Kihara, T., et al. (2000). FASEB J. 14, 1202–1214.
Linford, N. J. and Dorsa, D. M. (2002). Steroids 67, 1029–1040.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sawada, H., Shimohama, S. Estrogens and parkinson disease. Endocr 21, 77–79 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:21:1:77
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1385/ENDO:21:1:77