Abstract
Objective
To investigate the prognostic significance of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) in patients with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) treated with neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy (nCRT).
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed the charts of 416 consecutive patients with ESCC who underwent surgical resection following nCRT at the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital between 1998 and 2008. After exclusion of patients with non-R0 resection or showing no residual tumor (ypT0Nx), the histological tumor sections of 231 patients were reviewed for LVI. Univariate and multivariate analyses were used to identify the independent predictors of overall survival (OS).
Results
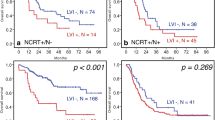
LVI was observed in 85 patients (36.8 %). The presence of LVI was related to close circumferential resection margins (CRMs), a greater depth of invasion, poor tumor differentiation, and an increased occurrence of lymph node metastases (LNM). The 5 year OS was significantly lower (10 %) in patients with LVI than in those without (31 %; p < 0.001). By multivariate Cox regression analyses, LVI (hazard ratio [HR] 1.5; p = 0.002) and LNM (HR 1.6; p = 0.007) were identified as independent adverse prognostic factors for OS. The 5 year OS rates according to the number of risk factors present were 35, 21, 20, and 5 for LVI(−)LNM(−), LVI(+)LNM(−), LVI(−)LNM(+), and LVI(+)LNM(+) patients, respectively (p < 0.001).
Conclusions
The presence of LVI is independently associated with shorter OS in ESCC patients receiving nCRT. Links between LVI and LNM may provide new clues for the prognostic stratification of esophageal cancer.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Enzinger PC, Mayer RJ. Esophageal cancer. N Engl J Med. 2003;349(23):2241–2252.
Sjoquist KM, Burmeister BH, Smithers BM, et al. Survival after neoadjuvant chemotherapy or chemoradiotherapy for resectable oesophageal carcinoma: an updated meta-analysis. Lancet Oncol. 2011;12(7):681-692.
Tong DKH, Law S, Kwong DLW, et al. Histological regression of squamous esophageal carcinoma assessed by percentage of residual viable cells after neoadjuvant chemoradiation is an important prognostic factor. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(8):2184-2192.
Swisher SG, Hofstetter W, Wu TT, et al. Proposed revision of the esophageal cancer staging system to accommodate pathologic response (pP) following preoperative chemoradiation (CRT). Ann Surg. 2005;241(5):810.
van Hagen P, Wijnhoven B, Nafteux P, et al. Recurrence pattern in patients with a pathologically complete response after neoadjuvant chemoradiotherapy and surgery for oesophageal cancer. Br J Surg. 2013;100(2):267-273.
Vallbohmer D, Holscher AH, DeMeester S, et al. A multicenter study of survival after neoadjuvant radiotherapy/chemotherapy and esophagectomy for ypT0N0M0R0 esophageal cancer. Ann Surg. 2010;252(5):744-749.
Rice TW, Blackstone EH, Rusch VW. 7th edition of the AJCC Cancer Staging Manual: esophagus and esophagogastric junction. Ann Surg Oncol. 2010;17(7):1721-1724.
Brücher BL, Stein HJ, Werner M, Siewert JR. Lymphatic vessel invasion is an independent prognostic factor in patients with a primary resected tumor with esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer. 2001;92(8):2228-2233.
Von Rahden BH, Stein HJ, Feith M, Becker K, Siewert JR. Lymphatic vessel invasion as a prognostic factor in patients with primary resected adenocarcinomas of the esophagogastric junction. J Clin Oncol. 2005;23(4):874-879.
Cen P, Hofstetter WL, Correa AM, et al. Lymphovascular invasion as a tool to further subclassify T1b esophageal adenocarcinoma. Cancer. 2008;112(5):1020-1027.
Mirnezami R, Rohatgi A, Sutcliffe RP, et al. Multivariate analysis of clinicopathological factors influencing survival following esophagectomy for cancer. Int J Surg. 2010;8(1):58-63.
Watanabe M, Kuwano H, Araki K, et al. Prognostic factors in patients with submucosal carcinoma of the oesophagus. Br J Cancer. 2000;83(5):609-613.
Van den Eynden G, Van der Auwera I, Van Laere S, et al. Distinguishing blood and lymph vessel invasion in breast cancer: a prospective immunohistochemical study. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(11):1643-1649.
Arame A, Mordant P, Cazes A, et al. Characteristics and prognostic value of lymphatic and blood vascular microinvasion in lung cancer. Ann Thorac Surg. 2012;94(5):1673-1679.
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by Grants NSC101-2314-B-182-094-MY2 (from the National Science Council, Executive Yuan, Taiwan, Republic of China) and NMRPD1B1432 (from the Chang Gung Memorial Hospital, Taiwan, Republic of China).
Conflicts of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, WH., Huang, YL., Chao, YK. et al. Prognostic Significance of Lymphovascular Invasion in Patients with Esophageal Squamous Cell Carcinoma Treated with Neoadjuvant Chemoradiotherapy. Ann Surg Oncol 22, 338–343 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3881-5
Received:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1245/s10434-014-3881-5