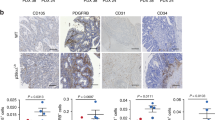
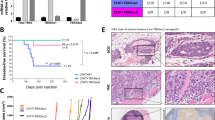
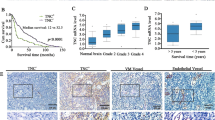
Abstract
TGF-β is a multifunctional cytokine affecting many cell types and implicated in tissue remodeling processes. Due to its many functions and cell-specific effects, the consequences of TGF-β signaling are process-and stage-dependent, and it is not uncommon that TGF-β exerts distinct and sometimes opposing effects on a disease progression depending on the stage and on the pathological changes associated with the stage. The mechanisms underlying cell- and process-specific effects of TGF-β are poorly understood. We are describing a novel pathway that mediates induction of angiogenesis in response to TGF-β1. We found that in endothelial cells (EC) thrombospondin-4 (TSP-4), a secreted extracellular matrix (ECM) protein, is upregulated in response to TGF-β1 and mediates the effects of TGF-β1 on angiogenesis. Upregulation of TSP-4 does not require the synthesis of new protein, is not caused by decreased secretion of TSP-4, and is mediated by activation of SMAD3. Using Thbs4−/− mice and TSP-4 shRNA, we found that TSP-4 mediated pro-angiogenic functions in cultured EC and angiogenesis in vivo in response to TGF-β1. We observed~3-fold increases in tumor mass and levels of angiogenesis markers in animals injected with TGF-β1, and these effects did not occur in Thbs4−/− animals. Injections of an inhibitor of TGF-β1 signaling SB-431542 also decreased the weights of tumors and cancer angiogenesis. Our results from in vivo angiogenesis models and cultured EC document that TSP-4 mediates upregulation of angiogenesis by TGF-β1. Upregulation of pro-angiogenic TSP-4 and selective effects of TSP-4 on EC may contribute to stimulation of tumor growth by TGF-β despite the inhibition of cancer cell proliferation.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 50 print issues and online access
$259.00 per year
only $5.18 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout








Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- bFGF:
-
basic fibroblasts growth factor
- DMSO:
-
dimethyl sulfoxide
- ECM:
-
extracellular matrix
- HDMEC:
-
human dermal microvascular endothelial cells
- HUVEC:
-
human umbilical vein endothelial cells
- IP:
-
intra-peritoneal
- KO:
-
knock-out
- MAEC:
-
mouse aortic endothelial cells
- MLEC:
-
mouse lung endothelial cells
- OCT:
-
OCT embedding cryoembedding Matrix
- shRNA:
-
small hairpin RNA
- VSMC:
-
vascular smooth muscle cells
- vWF:
-
von Willebrand factor
- WT:
-
wild type.
References
Hubmacher D, Apte SS . The biology of the extracellular matrix: novel insights. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2013; 25: 65–70.
Samarakoon R, Overstreet JM, Higgins PJ . TGF-beta signaling in tissue fibrosis: redox controls, target genes and therapeutic opportunities. Cell Signal 2013; 25: 264–268.
Lan HY, Chung AC . TGF-beta/Smad signaling in kidney disease. Semin Nephrol 2012; 32: 236–243.
Fernandez IE, Eickelberg O . The impact of TGF-beta on lung fibrosis: from targeting to biomarkers. Proc Am Thorac Soc 2012; 9: 111–116.
Weiss A, Attisano L . The TGFbeta superfamily signaling pathway. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 2013; 2: 47–63.
Katz LH, Li Y, Chen JS, Munoz NM, Majumdar A, Chen J et al. Targeting TGF-beta signaling in cancer. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2013; 17: 743–760.
Toma I, McCaffrey TA . Transforming growth factor-beta and atherosclerosis: interwoven atherogenic and atheroprotective aspects. Cell Tissue Res 2012; 347: 155–175.
Yang SN, Burch ML, Tannock LR, Evanko S, Osman N, Little PJ . Transforming growth factor-beta regulation of proteoglycan synthesis in vascular smooth muscle: contribution to lipid binding and accelerated atherosclerosis in diabetes. J Diabetes 2010; 2: 233–242.
Prendes MA, Harris A, Wirostko BM, Gerber AL, Siesky B . The role of transforming growth factor beta in glaucoma and the therapeutic implications. Br J Ophthalmol 2013; 97: 680–686.
Joseph JV, Balasubramaniyan V, Walenkamp A, Kruyt FA . TGF-beta as a therapeutic target in high grade gliomas - promises and challenges. Biochem Pharmacol 2013; 85: 478–485.
Yanagita M . Inhibitors/antagonists of TGF-beta system in kidney fibrosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2012; 27: 3686–3691.
Perrot CY, Javelaud D, Mauviel A . Overlapping activities of TGF-beta and Hedgehog signaling in cancer: therapeutic targets for cancer treatment. Pharmacol Ther 2013; 137: 183–199.
Araujo-Jorge TC, Waghabi MC, Bailly S, Feige JJ . The TGF-beta pathway as an emerging target for Chagas disease therapy. Clin Pharmacol Ther 2012; 92: 613–621.
Dietz HC . TGF-beta in the pathogenesis and prevention of disease: a matter of aneurysmic proportions. J Clin Invest 2010; 120: 403–407.
Muppala S, Frolova E, Xiao R, Krukovets I, Yoon S, Hoppe G et al. Proangiogenic properties of thrombospondin-4. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 2015; 35: 1975–1986.
Cho JY, Lim JY, Cheong JH, Park YY, Yoon SL, Kim SM et al. Gene expression signature-based prognostic risk score in gastric cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2011; 17: 1850–1857.
D'Errico M, de Rinaldis E, Blasi MF, Viti V, Falchetti M, Calcagnile A et al. Genome-wide expression profile of sporadic gastric cancers with microsatellite instability. Eur J Cancer 2009; 45: 461–469.
Singh D, Febbo PG, Ross K, Jackson DG, Manola J, Ladd C et al. Gene expression correlates of clinical prostate cancer behavior. Cancer Cell 2002; 1: 203–209.
Ma XJ, Wang Z, Ryan PD, Isakoff SJ, Barmettler A, Fuller A et al. A two-gene expression ratio predicts clinical outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. Cancer Cell 2004; 5: 607–616.
Curtis C, Shah SP, Chin SF, Turashvili G, Rueda OM, Dunning MJ et al. The genomic and transcriptomic architecture of 2,000 breast tumours reveals novel subgroups. Nature 2012; 486: 346–352.
Lu X, Wang ZC, Iglehart JD, Zhang X, Richardson AL . Predicting features of breast cancer with gene expression patterns. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2008; 108: 191–201.
Congote LF, Difalco MR, Gibbs BF . The C-terminal peptide of thrombospondin-4 stimulates erythroid cell proliferation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2004; 324: 673–678.
Frolova EG, Pluskota E, Krukovets I, Burke T, Drumm C, Smith JD et al. Thrombospondin-4 regulates vascular inflammation and atherogenesis. Circ Res 2010; 107: 1313–1325.
Mustonen E, Ruskoaho H, Rysa J . Thrombospondin-4, tumour necrosis factor-like weak inducer of apoptosis (TWEAK) and its receptor Fn14: novel extracellular matrix modulating factors in cardiac remodelling. Ann Med 2012; 44: 793–804.
Lynch JM, Maillet M, Vanhoutte D, Schloemer A, Sargent MA, Blair NS et al. A thrombospondin-dependent pathway for a protective ER stress response. Cell 2012; 149: 1257–1268.
Cingolani OH, Kirk JA, Seo K, Koitabashi N, Lee DI, Ramirez-Correa G et al. Thrombospondin-4 is required for stretch-mediated contractility augmentation in cardiac muscle. Circ Res 2011; 109: 1410–1414.
Loeys BL, Mortier G, Dietz HC . Bone lessons from Marfan syndrome and related disorders: fibrillin, TGF-B and BMP at the balance of too long and too short. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev 2013; 10: 417–423.
Yokoyama H, Deckert T . Central role of TGF-beta in the pathogenesis of diabetic nephropathy and macrovascular complications: a hypothesis. Diabet Med 1996; 13: 313–320.
Senger DR, Davis GE . Angiogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2011; 3: a005090.
Eming SA, Hubbell JA . Extracellular matrix in angiogenesis: dynamic structures with translational potential. Exp Dermatol 2011; 20: 605–613.
Kostourou V, Papalazarou V . Non-collagenous ECM proteins in blood vessel morphogenesis and cancer. Biochim Biophys Acta 2014; 1840: 2403–2413.
Verrecchia F, Mauviel A . Transforming growth factor-beta signaling through the Smad pathway: role in extracellular matrix gene expression and regulation. J Invest Dermatol 2002; 118: 211–215.
Yang Y, Zhou F, Fang Z, Wang L, Li Z, Sun L et al. Post-transcriptional and post-translational regulation of PTEN by transforming growth factor-beta1. J Cell Biochem 2009; 106: 1102–1112.
Hoover LL, Kubalak SW . Holding their own: the noncanonical roles of Smad proteins. Sci Signal 2008; 1: pe48.
Garcia R, Nistal JF, Merino D, Price NL, Fernandez-Hernando C, Beaumont J et al. p-SMAD2/3 and DICER promote pre-miR-21 processing during pressure overload-associated myocardial remodeling. Biochim Biophys Acta 2015; 1852: 1520–1530.
Davis BN, Hilyard AC, Lagna G, Hata A . SMAD proteins control DROSHA-mediated microRNA maturation. Nature 2008; 454: 56–61.
Chou YT, Yang YC . Post-transcriptional control of Cited2 by transforming growth factor beta. Regulation via Smads and Cited2 coding region. J Biol Chem 2006; 281: 18451–18462.
Blanco FF, Sanduja S, Deane NG, Blackshear PJ, Dixon DA . Transforming growth factor beta regulates P-body formation through induction of the mRNA decay factor tristetraprolin. Mol Cell Biol 2014; 34: 180–195.
Blahna MT, Hata A . Smad-mediated regulation of microRNA biosynthesis. FEBS Lett 2012; 586: 1906–1912.
Jinnin M, Ihn H, Tamaki K . Characterization of SIS3, a novel specific inhibitor of Smad3, and its effect on transforming growth factor-beta1-induced extracellular matrix expression. Mol Pharmacol 2006; 69: 597–607.
Krishnan S, Szabo E, Burghardt I, Frei K, Tabatabai G, Weller M . Modulation of cerebral endothelial cell function by TGF-beta in glioblastoma: VEGF-dependent angiogenesis versus endothelial mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget 2015; 6: 22480–22495.
James D, Nam HS, Seandel M, Nolan D, Janovitz T, Tomishima M et al. Expansion and maintenance of human embryonic stem cell-derived endothelial cells by TGFbeta inhibition is Id1 dependent. Nat Biotechnol 2010; 28: 161–166.
Petroll WM, Jester JV, Bean JJ, Cavanagh HD . Myofibroblast transformation of cat corneal endothelium by transforming growth factor-beta1, -beta2, and -beta3. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 1998; 39: 2018–2032.
Frolova EG, Sopko N, Blech L, Popovic ZB, Li J, Vasanji A et al. Thrombospondin-4 regulates fibrosis and remodeling of the myocardium in response to pressure overload. FASEB J 2012; 26: 2363–2373.
Mahabeleshwar GH, Somanath PR, Byzova TV . Methods for isolation of endothelial and smooth muscle cells and in vitro proliferation assays. Methods Mol Med 2006; 129: 197–208.
Soloviev DA, Pluskota E, Plow EF . Cell adhesion and migration assays. Methods Mol Med 2006; 129: 267–278.
Stenina OI, Desai SY, Krukovets I, Kight K, Janigro D, Topol EJ et al. Thrombospondin-4 and its variants: expression and differential effects on endothelial cells. Circulation 2003; 108: 1514–1519.
Bhattacharyya S, Sul K, Krukovets I, Nestor C, Li J, Adognravi OS . Novel tissue-specific mechanism of regulation of angiogenesis and cancer growth in response to hyperglycemia. J Am Heart Assoc 2012; 1: e005967.
Bhattacharyya S, Marinic TE, Krukovets I, Hoppe G, Stenina OI . Cell type-specific post-transcriptional regulation of production of the potent antiangiogenic and proatherogenic protein thrombospondin-1 by high glucose. J Biol Chem 2008; 283: 5699–5707.
Acknowledgements
This work was supported by NIH R01HL117216 (OS-A and EP) and NIH CA177771 (OS-A). Isolation of HUVECs was supported by UL1TR000439. HUVECs were provided by a grant awarded to Clinical and Translational Science Collaborative of Cleveland, a grant from the National Center for Advancing Translational Sciences (UL1TR000439) component of the National Institutes of Health, and National Institutes of Health Roadmap for Medical Research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Supplementary Information accompanies this paper on the Oncogene website
Supplementary information
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muppala, S., Xiao, R., Krukovets, I. et al. Thrombospondin-4 mediates TGF-β-induced angiogenesis. Oncogene 36, 5189–5198 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.140
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2017.140
This article is cited by
-
Epigenetics and stroke: role of DNA methylation and effect of aging on blood–brain barrier recovery
Fluids and Barriers of the CNS (2023)
-
Targeting TGF-β signal transduction for fibrosis and cancer therapy
Molecular Cancer (2022)
-
TGF-beta signal transduction: biology, function and therapy for diseases
Molecular Biomedicine (2022)
-
Culturing of Cardiac Cells in 3D Spheroids Modulates Their Expression Profile and Increases Secretion of Proangiogenic Growth Factors
Bulletin of Experimental Biology and Medicine (2022)
-
Thrombospondin 4/integrin α2/HSF1 axis promotes proliferation and cancer stem-like traits of gallbladder cancer by enhancing reciprocal crosstalk between cancer-associated fibroblasts and tumor cells
Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research (2021)