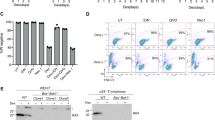
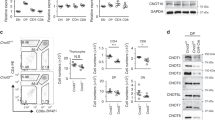
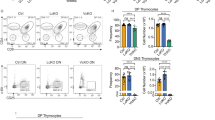
Abstract
APOPTOSIS is a phenomenon observed during development of many cell types in many organisms. It is an internal, programmed cell death characterized by DNA fragmentation into nucleosome-size pieces1–3. Anti-CD3-induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas and immature thymocytes requires new gene transcription and may be related to negative selection during T-cell development4–6. Using subtractive hybridization, we isolated a complementary DNA clone encoding the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 (refs 7–9). It shows different patterns of messenger RNA induction between apoptotic and stimulated T cells. We report here the use of gel shift analysis to demonstrate that the Nur77 protein is present at high levels in apoptotic T-cell hybridomas and apoptotic thymocytes, but not in growing T cells or stimulated splenocytes. A Nur77 dominant negative protected T-cell hybridomas from activation-induced apoptosis. Hence Nur77 is necessary for induced apoptosis in T-cell hybridomas.
This is a preview of subscription content, access via your institution
Access options
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
$199.00 per year
only $3.90 per issue
Buy this article
- Purchase on Springer Link
- Instant access to full article PDF
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen, J. J., Duke, R. C., Fadok, V. A. & Sellins, K. S. A. Rev. Immun. 10, 267–293 (1992).
Oppenheim, R. W. A. Rev. Neurosci. 14, 453–501 (1991).
Kerr, J. F. R. & Harmon, B. V. in Apoptosis: the Molecular Basis of Cell Death (eds Tomei, L. D. & Cope, F. O.) 5–29 (Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press, New York, 1991).
Mercep, M., Noguchi, P. D. & Ashwell, J. D. J. Immun. 142, 4085–4092 (1989).
Shi, Y. F. et al. J. Immun. 144, 3326–3333 (1990).
Smith, C. A. et al. Nature 337, 181–184 (1989).
Christy, B. A., Lau, L. F. & Nathans, D. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 7857–7861 (1988).
Milbrandt, J. Neuron 1, 183–188 (1988).
Ryseck, R. P. et al. EMBO J. 8, 3327–3335 (1989).
Shastri, N., Gammon, G., Miller, A. & Sercarz, E. E. J. exp. Med. 164, 882–896 (1986).
Hazel, T. G., Nathans, D. & Lau, L. F. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 8444–8448 (1988).
Watson, M. A. & Milbrandt, J. Molec. cell. Biol. 9, 4213–4219 (1989).
Milbrandt, J. Science 238, 797–799 (1987).
Sukhatme, V. P. et al. Cell 53, 37–43 (1988).
Lemaire, P., Revelant, O., Bravo, R. & Charnay, P. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 85, 4691–4695 (1988).
Christy, B. A. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 1815–1819 (1991).
Wilson, T. E., Fahrner, T. J., Johnston, M. & Milbrandt, J. Science 252, 1296–1300 (1991).
Wilson, T. E., Paulsen, R. E., Padgett, K. A. & Milbrandt, J. Science 256, 107–110 (1992).
Kingsley, C. & Winoto, A. Molec. cell. Biol. 12, 4251–4261 (1992).
Karasuyama, H. & Melchers, F. Eur. J. Immun. 18, 97–104 (1988).
Shaw, P. et al. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 89, 4495–4499 (1992).
Yonish, R. E. et al. Nature 353, 345–347 (1991).
Lowe, S. W. et al. Nature 362, 847–849 (1993).
Evan, G. I. et al. Cell 69, 119–128 (1992).
Shi, Y. et al. Science 257, 212–214 (1992).
Korsmeyer, S. J. Immun. Today 13, 285–288 (1992).
Ishida, Y., Agata, Y., Shibahara, K. & Honjo, T. EMBO J. 11, 3887–3895 (1992).
Cohen, P. L. & Eisenberg, R. A. Immun. Today 13, 427–428 (1992).
Sentman, C. L. et al. Cell 67, 879–888 (1991).
Matthias, P. et al. Nucleic Acids Res. 17, 6418 (1989).
Marine, J. & Winoto, A. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 88, 7284–7288 (1991).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Woronicz, J., Calnan, B., Ngo, V. et al. Requirement for the orphan steroid receptor Nur77 in apoptosis of T-cell hybridomas. Nature 367, 277–281 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1038/367277a0
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1038/367277a0
This article is cited by
-
Drug targeting of NR4A nuclear receptors for treatment of acute myeloid leukemia
Leukemia (2019)
-
SUMO-triggered ubiquitination of NR4A1 controls macrophage cell death
Cell Death & Differentiation (2017)
-
Expression of Twist2 is controlled by T-cell receptor signaling and determines the survival and death of thymocytes
Cell Death & Differentiation (2016)
-
TR3 is preferentially expressed by bulge epithelial stem cells in human hair follicles
Laboratory Investigation (2016)
-
Transcriptional modulation of regulatory T cell development by novel regulators NR4As
Archives of Pharmacal Research (2016)
Comments
By submitting a comment you agree to abide by our Terms and Community Guidelines. If you find something abusive or that does not comply with our terms or guidelines please flag it as inappropriate.