Abstract
Haematological malignancies, including acute leukaemia and non-Hodgkin lymphoma, are one of the underlying diseases that frequently cause disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC), an acquired thrombotic disorder. Concomitant DIC is associated with the severity of the underlying disease and poor prognosis. The Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis released the new DIC diagnostic criteria in 2017. This criteria include coagulation markers such as soluble fibrin and the thrombin-antithrombin complex to more accurately evaluate the hypercoagulable state in patients. Among several groups of anticoagulants available, recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin is most frequently used to treat DIC caused by haematological malignancies in Japan. DIC is remitted in parallel with the improvement of the underlying haematological diseases; thus, there is room for debate regarding whether the treatment of DIC would improve the prognosis of patients. Haematopoietic stem cell transplantation as well as the recently introduced chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T-cell therapy are innovative therapies to produce a cure in a subset of patients with haematological malignancies. However, coagulopathy frequently occurs after these therapies, which limits the success of the treatment. For example, DIC is noted in approximately 50% of patients after CAT-T-cell therapy in conjunction with cytokine release syndrome. Hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) causes endotheliitis, which triggers coagulopathy and the development of potentially lethal complications, such as sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease and transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. This review article describes the pathogenesis, clinical manifestation, diagnosis, and treatment of DIC caused by haematological malignancies, CAR-T-cell therapy, and HSCT.

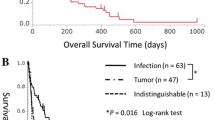
This figure is adapted from Ref. [5]

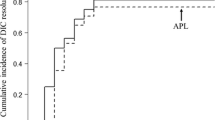
This figure is adapted from Ref. [26]


This figure is adapted from Ref. [3]

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Okajima K, Sakamoto Y, Uchiba M. Heterogeneity in the incidence and clinical manifestations of disseminated intravascular coagulation: a study of 204 cases. Am J Hematol. 2000;65(3):215–22.
Singh B, Hanson AC, Alhurani R, Wang S, Herasevich V, Cartin-Ceba R, et al. Trends in the incidence and outcomes of disseminated intravascular coagulation in critically ill patients (2004-2010): a population-based study. Chest. 2013;143(5):1235–42.
Ikezoe T. Pathogenesis of disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia, and its treatment using recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Int J Hematol. 2014;100(1):27–37.
Uchiumi H, Matsushima T, Yamane A, Doki N, Irisawa H, Saitoh T, et al. Prevalence and clinical characteristics of acute myeloid leukemia associated with disseminated intravascular coagulation. Int J Hematol. 2007;86(2):137–42.
Chi S, Ikezoe T. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Int J Hematol. 2015;102(4):413–9.
Carreras E, Diaz-Ricart M. The role of the endothelium in the short-term complications of hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2011;46(12):1495–502.
Carreras E, Diaz-Ricart M. Early complications of endothelial origin. The EBMT handbook: hematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapies [Internet]. 7 Chapter 42. ed. Cham: Springer; 2019. p. 315–22.
Falanga A, Iacoviello L, Evangelista V, Consonni R, Belotti D, D’Orazio A, et al. Loss of blast cell procoagulant activity and improvement of hemostatic variables in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia given all-trans-retinoic acid. Blood. 1995;86:1072.
Bauer KA, Rosenberg RD. Thrombin generation in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Blood. 1984;64:791.
Mjers TJ, Rickles FR, Barb C, Cronlund M. Fibrinopeptide A in acute leukemia: relationship of activation of blood coagulation to disease activity. Blood. 1981;57:518.
Dicke C, Amirkhosravi A, Spath B, Jiménez-Alcázar M, Fuchs T, Davila M, Francis JL, Bokemeyer C, Langer F. Tissue factor-dependent and -independent pathways of systemic coagulation activation in acute myeloid leukemia: a single-center cohort study. Exp Hematol Oncol. 2015;6(4):22.
Sase T, Wada H, Yamaguchi M, Ogawa S, Kamikura Y, Nishikawa M, et al. Haemostatic abnormalities and thrombotic disorders in malignant lymphoma. Thromb Haemost. 2005;93(1):153–9.
Falanga A, Gordon SG. Isolation and characterization of cancer procoagulant: a cysteine proteinase from malignant tissue. Biochemistry. 1985;24:5558–67.
Falanga A, Alessio MG, Donati MB, Barbui T. A new procoagulant in acute leukemia. Blood. 1988;71:870–5.
Wang H, Bloom O, Zhang M, Vishnubhakat JM, Ombrellino M, Che J, et al. HMG-1 as a late mediator of endotoxin lethality in mice. Science. 1999;285(5425):248–51.
Ito T, Kawahara K, Nakamura T, Yamada S, Nakamura T, Abeyama K, et al. High-mobility group box 1 protein promotes development of microvascular thrombosis in rats. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(1):109–16.
Fuchs TA, Brill A, Duerschmied D, Schatzberg D, Monestier M, Myers DD Jr, et al. Extracellular DNA traps promote thrombosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 2010;107(36):15880–5.
Xu J, Zhang X, Pelayo R, Monestier M, Ammollo CT, Semeraro F, et al. Extracellular histones are major mediators of death in sepsis. Nat Med. 2009;15(11):1318–21.
McDonald B, Davis RP, Kim SJ, Tse M, Esmon CT, Kolaczkowska E, et al. Platelets and neutrophil extracellular traps collaborate to promote intravascular coagulation during sepsis in mice. Blood. 2017;129(10):1357–67.
Nakahara M, Ito T, Kawahara K, Yamamoto M, Nagasato T, Shrestha B, et al. Recombinant thrombomodulin protects mice against histone-induced lethal thromboembolism. PLoS One. 2013;8(9):e75961.
Semeraro F, Ammollo CT, Morrissey JH, Dale GL, Friese P, Esmon NL, et al. Extracellular histones promote thrombin generation through platelet-dependent mechanisms: involvement of platelet TLR2 and TLR4. Blood. 2011;118(7):1952–61.
Harada-Shirado K, Wang X, Mori H, Fukatsu M, Takahashi H, Shichishima-Nakamura A, et al. Circulating intranuclear proteins may play a role in development of disseminated intravascular coagulation in individuals with acute leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2020;111(3):378–87.
Gando S, Levi M, Toh CH. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Nat Rev Dis Primers. 2016;2:16037. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.37.
Tipoe TL, Wu WKK, Chung L, Gong M, Dong M, Liu T, et al. Plasminogen activator inhibitor 1 for predicting sepsis severity and mortality outcomes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Front Immunol. 2018;9:1218. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01218.
Huang D, Yang Y, Sun J, Dong X, Wang J, Liu H, et al. Annexin A2-S100A10 heterotetramer is upregulated by PML/RARα fusion protein and promotes plasminogen-dependent fibrinolysis and matrix invasion in acute promyelocytic leukemia. Front Med. 2017;11(3):410–22.
Menell JS, Cesarman GM, Jacovina AT, McLaughlin MA, Lev EA, Hajjar KA. Annexin II and bleeding in acute promyelocytic leukemia. N Engl J Med. 1999;340(13):994–1004.
O’Connell PA, Madureira PA, Berman JN, Liwski RS, Waisman DM. Regulation of S100A10 by the PML-RAR-α oncoprotein. Blood. 2011;117(15):4095–105.
Godier A, Hunt BJ. Plasminogen receptors and their role in the pathogenesis of inflammatory, autoimmune and malignant disease. J Thromb Haemost. 2013;11(1):26–34.
Tapiovaara H, Alitalo R, Stephens R, Myöhänen H, Ruutu T, Vaheri A. Abundant urokinase activity on the surface of mononuclear cells from blood and bone marrow of acute leukemia patients. Blood. 1993;82:914–9.
Nadir Y, Katz T, Sarig G, Hoffman R, Oliven A, Rowe JM. Hemostatic balance on the surface of leukemic cells: the role of tissue factor and urokinase plasminogen activator receptor. Haematologica. 2005;90:1549–56.
Niiya K, Ozawa T, Tsuzawa T, Ueshima S, Matsuo O, Sakuragawa N. Transcriptional regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor by cyclic AMP in PL-21 human myeloid leukemia cells: comparison with the regulation by phorbol myristate acetate. Thromb Haemost. 1998;79(3):574–8.
Pluchart C, Poitevin G, Colinart-Thomas M, Guimard G, Audonnet S, et al. Vincristine induces procoagulant activity of the human lymphoblastic leukemia cell line Jurkat through the release of extracellular vesicles. J Thromb Thrombolysis. 2019;48(2):195–202.
Kubota T, Andoh K, Sadakata H, Tanaka H, Kobayashi N. Tissue factor released from leukemic cells. Thromb Haemost. 1991;65(1):59–63.
Walsh J, Wheeler HR, Geczy CL. Modulation of tissue factor on human monocytes by cisplatin and adriamycin. Br J Haematol. 1992;81(4):480–8.
de la Serna J, Montesinos P, Vellenga E, Rayón C, Parody R, León A, et al. Causes and prognostic factors of remission induction failure in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia treated with all-trans retinoic acid and idarubicin. Blood. 2008;111(7):3395–402.
Di Bona E, Avvisati G, Castaman G, Luce Vegna M, De Sanctis V, et al. Early haemorrhagic morbidity and mortality during remission induction with or without all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukaemia. Br J Haematol. 2000;108(4):689–95.
Kim H, Lee JH, Choi SJ, Lee JH, Seol M, Lee YS, Kim WK, Lee JS, Lee KH. Risk score model for fatal intracranial hemorrhage in acute leukemia. Leukemia. 2006;20(5):770–6.
Ichikawa K, Edahiro Y, Gotoh A, Iiduka K, Komatsu N, Koike M. Co-occurrence of hyperleukocytosis and elevated fibrin-fibrinogen degradation product levels is a risk factor for early intracranial hemorrhage in patients with de novo acute leukemia. Int J Hematol. 2016;104(5):612–20.
Breccia M, Avvisati G, Latagliata R, Carmosino I, Guarini A, De Propris MS, et al. Occurrence of thrombotic events in acute promyelocytic leukemia correlates with consistent immunophenotypic and molecular features. Leukemia. 2007;21:79–83.
Kojima S, Nishioka C, Chi S, Yokoyama A, Ikezoe T. In vitro studies on the role of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin in the context of retinoic acid mediated APL differentiation syndrome. Leuk Res. 2017;63:1–9.
Hashimoto S, Koike T, Tatewaki W, Seki Y, Sato N, Azegami T, et al. Fatal thromboembolism in acute promyelocytic leukemia during all-trans retinoic acid therapy combined with antifibrinolytic therapy for prophylaxis of hemorrhage. Leukemia. 1994;8(7):1113–5.
Tsukada N, Wada K, Aoki S, Hashimoto S, Kishi K, Takahashi M, et al. Induction therapy with all-trans retinoic acid for acute promyelocytic leukemia: a clinical study of 10 cases, including a fatal [correction of fetal] case with thromboembolism. Intern Med. 1996;35(1):10–4.
Asakura H, Takahashi H, Uchiyama T, Eguchi Y, Okamoto K, Kawasugi K, et al. Proposal for new diagnostic criteria for DIC from the Japanese Society on Thrombosis and Hemostasis. Thromb J. 2016;14:42.
Asakura H, Takahashi H, Tsuji H, Matsushita T, Ninomiya H, Honda G, et al. Post-marketing surveillance of thrombomodulin alfa, a novel treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation—safety and efficacy in 1,032 patients with hematologic malignancy. Thromb Res. 2014;133(3):364–70.
Osone S, Fukushima K, Yano M, Kakazu M, Sano H, Kato Y, et al. Supportive care for hemostatic complications associated with pediatric leukemia: a national survey in Japan. Int J Hematol. 2019;110(6):743–50.
Ikezoe T. Thrombomodulin/activated protein C system in septic disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Intensive Care. 2015;3(1):1.
Mosnier LO, Meijers JC, Bouma BN. Regulation of fibrinolysis in plasma by TAFI and protein C is dependent on the concentration of thrombomodulin. Thromb Haemost. 2001;85:5–11.
Abeyama K, Stern DM, Ito Y, Kawahara K, Yoshimoto Y, Tanaka M, et al. The N-terminal domain of thrombomodulin sequesters high-mobility group-B1 protein, a novel antiinflammatory mechanism. J Clin Investig. 2005;115:1267–74.
Pan B, Wang X, Nishioka C, Honda G, Yokoyama A, Zeng L, et al. G-protein coupled receptor 15 mediates angiogenesis and cytoprotective function of thrombomodulin. Sci Rep. 2017;7(1):692.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Honda G, Furihata M, Yokoyama A. Thrombomodulin protects endothelial cells from a calcineurin inhibitor-induced cytotoxicity by upregulation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase/myeloid leukemia cell-1 signaling. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2012;32(9):2259–70.
Pan B, Wang X, Kojima S, Nishioka C, Yokoyama A, Honda G, et al. The fifth epidermal growth factor like region of thrombomodulin alleviates LPS-induced sepsis through interacting with GPR15. Thromb Haemost. 2017;117(3):570–9.
Pan B, Wang X, Kojima S, Nishioka C, Yokoyama A, Honda G, et al. The fifth epidermal growth factor-like region of thrombomodulin alleviates murine graft-versus-host disease in a G-protein coupled receptor 15 dependent manner. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2017;23(5):746–56.
Saito H, Maruyama I, Shimazaki S, Yamamoto Y, Aikawa N, Ohno R, et al. Efficacy and safety of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin (ART-123) in disseminated intravascular coagulation: results of a phase III, randomized, double-blind clinical trial. J Thromb Haemost. 2007;5(1):31–41.
Matsushita T, Watanabe J, Honda G, Mimuro J, Takahashi H, Tsuji H, et al. Thrombomodulin alfa treatment in patients with acute promyelocytic leukemia and disseminated intravascular coagulation: a retrospective analysis of an open-label, multicenter, post-marketing surveillance study cohort. Thromb Res. 2014;133(5):772–81.
Ikezoe T, Takeuchi A, Isaka M, Arakawa Y, Iwabu N, Kin T, et al. Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin safely and effectively rescues acute promyelocytic leukemia patients from disseminated intravascular coagulation. Leuk Res. 2012;36(11):1398–402.
Kawano N, Kuriyama T, Yoshida S, Yamashita K, Ochiai H, Nakazaki S, et al. Clinical features and treatment outcomes of six patients with disseminated intravascular coagulation resulting from acute promyelocytic leukemia and treated with recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin at a single institution. Intern Med. 2013;52(1):55–62.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Isaka M, Iwabu N, Sakai M, et al. Thrombomodulin enhances the antifibrinolytic and antileukemic effects of all-trans retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia cells. Exp Hematol. 2012;40(6):457–65.
Takezako N, Sekiguchi N, Nagata A, Homma C, Takezako Y, Noto S, et al. Recombinant human thrombomodulin in the treatment of acute myeloid leukemia patients complicated by disseminated intravascular coagulation: retrospective analysis of outcomes between patients treated with heparin and recombinant human thrombomodulin therapy. Thromb Res. 2015;136(1):20–3.
Minakata D, Fujiwara SI, Ikeda T, Kawaguchi SI, Toda Y, Ito S, et al. Comparison of gabexate mesilate and nafamostat mesilate for disseminated intravascular coagulation associated with hematological malignancies. Int J Hematol. 2019;109(2):141–6.
Jackson HJ, Rafiq S, Brentjens RJ. Driving CAR T-cells forward. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2016;13(6):370–83.
Schuster SJ, Maziarz RT, Rusch ES, Li J, Signorovitch JE, Romanov VV, et al. Grading and management of cytokine release syndrome in patients treated with tisagenlecleucel in the JULIET trial. Blood Adv. 2020;4(7):1432–9.
Jiang H, Liu L, Guo T, Wu Y, Ai L, Deng J, Dong J, Mei H, Hu Y. Improving the safety of CAR-T cell therapy by controlling CRS-related coagulopathy. Ann Hematol. 2019;98(7):1721–32.
Wang Y, Qi K, Cheng H, Cao J, Shi M, Qiao J, et al. Coagulation disorders after chimeric antigen receptor T cell therapy: analysis of 100 patients with relapsed and refractory hematologic malignancies. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2020;26(5):865–75.
Taylor FB Jr, Toh C-H, Hoots KW, Wada H, Levi M. Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:1327–30.
Ikezoe T, Takeuchi A, Chi S, Takaoka M, Anabuki K, Kim T, et al. Effect of recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin on clinical outcomes of patients with coagulopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Eur J Haematol. 2013;91(5):442–7.
Matsumoto T, Wada H, Nishiyama H, Hirano T, Sakakura M, Nishii K, et al. Hemostatic abnormalities and changes following bone marrow transplantation. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 2004;10:341–50.
Mohty M, Malard F, Abecasis M, Aerts E, Alaskar AS, Aljurf M, et al. Prophylactic, preemptive, and curative treatment for sinusoidal obstruction syndrome/veno-occlusive disease in adult patients: a position statement from an international expert group. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2020;55(3):485–95.
DeLeve LD, Ito Y, Bethea NW, et al. Embolization by sinusoidal lining cells obstructs the microcirculation in rat sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2003;284:G1045–52.
Corbacioglu S, Jabbour EJ, Mohty M. Risk factors for development of and progression of hepatic veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant. 2019;25(7):1271–80.
Ikezoe T, Togitani K, Komatsu N, Isaka M, Yokoyama A. Successful treatment of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2010;45(4):783–5.
Ohwada C, Takeuchi M, Kawaguchi T, Tsukamoto S, Sakai S, Takeda Y, et al. Successful treatment with recombinant soluble thrombomodulin of two cases of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome/hepatic veno-occlusive disease after bone marrow transplantation. Am J Hematol. 2011;86(10):886–8.
Nakamura D, Yoshimitsu M, Kawada H, Inoue H, Kuroki T, Kaieda T, et al. Recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin for the treatment of hepatic sinusoidal obstructive syndrome post allogeneic hematopoietic SCT. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2012;47(3):463–4.
Inagaki J, Kurauchi K, Fukano R, Noguchi M, Okamura J. Heterogeneous response to recombinant thrombomodulin by grade of sinusoidal obstructive syndrome after pediatric stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2016;51(11):1543–5.
Yakushijin K, Ikezoe T, Ohwada C, Kudo K, Okamura H, Goto H, et al. Clinical effects of recombinant thrombomodulin and defibrotide on sinusoidal obstruction syndrome after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54(5):674–80.
Ikezoe T, Yang J, Nishioka C, Pan B, Xu K, Furihata M, et al. The fifth epidermal growth factor-like region of thrombomodulin exerts cytoprotective function and prevents SOS in a murine model. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(1):73–9.
Wang X, Pan B, Honda G, Wang X, Hashimoto Y, Ohkawara H, et al. Cytoprotective and pro-angiogenic functions of thrombomodulin are preserved in the C loop of the fifth epidermal growth factor-like domain. Haematologica. 2018;103(10):1730–40.
Richardson P, Aggarwal S, Topaloglu O, Villa KF, Corbacioglu S. Systematic review of defibrotide studies in the treatment of veno-occlusive disease/sinusoidal obstruction syndrome (VOD/SOS). Bone Marrow Transplant. 2019;54(12):1951–62.
Evangelista V, Piccardoni P, de Gaetano G, Cerletti C. Defibrotide inhibits platelet activation by cathepsin G released from stimulated polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Thromb Haemost. 1992;67(6):660–4.
Paul W, Gresele P, Momi S, Bianchi G, Page CP. The effect of defibrotide on thromboembolism in the pulmonary vasculature of mice and rabbits and in the cerebral vasculature of rabbits. Br J Pharmacol. 1993;110(4):1565–71.
Falanga A, Vignoli A, Marchetti M, Barbui T. Defibrotide reduces procoagulant activity and increases fibrinolytic properties of endothelial cells. Leukemia. 2003;17(8):1636–42.
Schoergenhofer C, Buchtele N, Gelbenegger G, Derhaschnig U, Firbas C, Kovacevic KD, et al. Defibrotide enhances fibrinolysis in human endotoxemia—a randomized, double blind, crossover trial in healthy volunteers. Sci Rep. 2019;9(1):11136.
Wang X, Pan B, Hashimoto Y, Ohkawara H, Xu K, Zeng L, et al. Defibrotide stimulates angiogenesis and protects endothelial cells from calcineurin inhibitor-induced apoptosis via upregulation of AKT/Bcl-xL. Thromb Haemost. 2018;118(1):161–73.
Khosla J, Yeh AC, Spitzer TR, Dey BR. Hematopoietic stem cell transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: current paradigm and novel therapies. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2018;53(2):129–37.
Zeigler ZR, Rosenfeld CS, Andrews DF 3rd, Nemunaitis J, Raymond JM, Shadduck RK, et al. Plasma von Willebrand factor antigen (vWF:AG) and thrombomodulin (TM) levels in adult thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura/hemolytic uremic syndromes (TTP/HUS) and bone marrow transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy (BMT-TM). Am J Hematol. 1996;53(4):213–20.
Takatsuka H, Wakae T, Mori A, Okada M, Suehiro A, Okamoto T, et al. Thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura and hemolytic uremic syndrome following allogeneic bone marrow transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2002;29(11):907–11.
Chua JS, Baelde HJ, Zandbergen M, Wilhelmus S, van Es LA, et al. Complement factor C4d is a common denominator in thrombotic microangiopathy. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2015;26(9):2239–47.
Noris M, Remuzzi G. Atypical hemolytic-uremic syndrome. N Engl J Med. 2009;361(17):1676–87.
Jodele S, Medvedovic M, Luebbering N, Chen J, Dandoy CE, Laskin BL, et al. Interferon-complement loop in transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy. Blood Adv. 2020;4(6):1166–77.
Jodele S, Davies SM, Lane A, Khoury J, Dandoy C, Goebel J, et al. Diagnostic and risk criteria for HSCT-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a study in children and young adults. Blood. 2014;124(4):645–53.
Atefi G, Aisiku O, Shapiro N, et al. Complement activation in trauma patients alters platelet function. Shock. 2016;46:83–8.
Mizuno T, Yoshioka K, Mizuno M, et al. Complement component 5 promotes lethal thrombosis. Sci Rep. 2017;7:42714.
Subramaniam S, Jurk K, Hobohm L, Jäckel S, Saffarzadeh M, Schwierczek K, et al. Distinct contributions of complement factors to platelet activation and fibrin formation in venous thrombus development. Blood. 2017;129(16):2291–302.
Yeates L, Slatter MA, Bonanomi S, Lim FLWI, Ong SY, Dalissier A, et al. Use of defibrotide to treat transplant-associated thrombotic microangiopathy: a retrospective study of the Paediatric Diseases and Inborn Errors Working Parties of the European Society of Blood and Marrow Transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(5):762–4.
Fujiwara H, Maeda Y, Sando Y, Nakamura M, Tani K, Ishikawa T, et al. Treatment of thrombotic microangiopathy after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation with recombinant human soluble thrombomodulin. Transfusion. 2016;56(4):886–92.
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by KAKENHI (18H02844) to Ikezoe T.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Ikezoe T receives a research fund form Asahi Kasei Pharma and Nihon Shinyaku Co., Ltd.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
About this article
Cite this article
Ikezoe, T. Advances in the diagnosis and treatment of disseminated intravascular coagulation in haematological malignancies. Int J Hematol 113, 34–44 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-020-02992-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s12185-020-02992-w