Abstract
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a result of the atherosclerotic narrowing of blood vessels to the extremities, and the subsequent tissue ischemia can lead to the up-regulation of angiogenic growth factors and formation of new vessels as a recovery mechanism. Such formation of new vessels can be evaluated with various non-invasive molecular imaging techniques, where serial images from the same subjects can be obtained to allow the documentation of disease progression and therapeutic response. The most commonly used animal model for preclinical studies of PAD is the murine hindlimb ischemia model, and a number of radiotracers have been investigated for positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging of PAD. In this review article, we summarize the PET/SPECT tracers that have been tested in the murine hindlimb ischemia model as well as those used clinically to assess the extremity blood flow.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sumner AD, Khalil YK, Reed JF 3rd (2012) The relationship of peripheral arterial disease and metabolic syndrome prevalence in asymptomatic US adults 40 years and older: results from the National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey (1999–2004). J Clin Hypertens (Greenwich) 14:144–148
van Weel V, van Tongeren RB, van Hinsbergh VW, van Bockel JH, Quax PH (2008) Vascular growth in ischemic limbs: a review of mechanisms and possible therapeutic stimulation. Ann Vasc Surg 22:582–597
Clair D, Shah S, Weber J (2012) Current state of diagnosis and management of critical limb ischemia. Curr Cardiol Rep 14:160–170
Hinchliffe RJ, Andros G, Apelqvist J, Bakker K, Friederichs S, Lammer J et al (2012) A systematic review of the effectiveness of revascularization of the ulcerated foot in patients with diabetes and peripheral arterial disease. Diabetes Metab Res Rev 28(Suppl 1):179–217
Ouriel K (2001) Peripheral arterial disease. Lancet 358:1257–1264
Andersen CA (2010) Noninvasive assessment of lower extremity hemodynamics in individuals with diabetes mellitus. J Vasc Surg 52:76S–80S
Mathieu D, Mani R (2007) A review of the clinical significance of tissue hypoxia measurements in lower extremity wound management. Int J Low Extrem Wounds 6:273–283
Tang GL, Chin J, Kibbe MR (2010) Advances in diagnostic imaging for peripheral arterial disease. Expert Rev Cardiovasc Ther 8:1447–1455
Galbraith JE, Murphy ML, de Soyza N (1978) Coronary angiogram interpretation. Interobserver variability. JAMA 240:2053–2056
Leape LL, Park RE, Bashore TM, Harrison JK, Davidson CJ, Brook RH (2000) Effect of variability in the interpretation of coronary angiograms on the appropriateness of use of coronary revascularization procedures. Am Heart J 139:106–113
Cavalcanti Filho JL, de Souza Leao Lima R, de Souza Machado Neto L, Kayat Bittencourt L, Domingues RC, da Fonseca LM (2011) PET/CT and vascular disease: current concepts. Eur J Radiol 80:60–67
Dobrucki LW, Sinusas AJ (2007) Imaging angiogenesis. Curr Opin Biotechnol 18:90–96
Suh JW, Scheinost D, Dione DP, Dobrucki LW, Sinusas AJ, Papademetris X (2011) A non-rigid registration method for serial lower extremity hybrid SPECT/CT imaging. Med Image Anal 15:96–111
Cai W, Chen X (2007) Multimodality imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor and vascular endothelial growth factor receptor expression. Front Biosci 12:4267–4279
Cai W, Chen X (2008) Multimodality molecular imaging of tumor angiogenesis. J Nucl Med 49(Suppl 2):113S–128S
Waters RE, Terjung RL, Peters KG, Annex BH (2004) Preclinical models of human peripheral arterial occlusive disease: implications for investigation of therapeutic agents. J Appl Physiol 97:773–780
Couffinhal T, Silver M, Zheng LP, Kearney M, Witzenbichler B, Isner JM (1998) Mouse model of angiogenesis. Am J Pathol 152:1667–1679
Niiyama H, Huang NF, Rollins MD, Cooke JP (2009) Murine model of hindlimb ischemia. J Vis Exp 23:1035. doi:10.3791/1035
James ML, Gambhir SS (2012) A molecular imaging primer: modalities, imaging agents, and applications. Physiol Rev 92:897–965
Ubbink DT, Tulevski II, den Hartog D, Koelemay MJ, Legemate DA, Jacobs MJ (1997) The value of non-invasive techniques for the assessment of critical limb ischaemia. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 13:296–300
Alauddin MM (2012) Positron emission tomography (PET) imaging with 18F-based radiotracers. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:55–76
Vach W, Høilund-Carlsen PF, Fischer BM, Gerke O, Weber W (2011) How to study optimal timing of PET/CT for monitoring of cancer treatment. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 1:54–62
Zeman MN, Scott PJH (2012) Current imaging strategies in rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:174–220
Bhargava P, He G, Samarghandi A, Delpassand ES (2012) Pictorial review of SPECT/CT imaging applications in clinical nuclear medicine. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:221–231
Ogasawara Y, Ogasawara K, Suzuki T, Yamashita T, Kuroda H, Chida K et al (2012) Preoperative 123I-iomazenil SPECT imaging predicts cerebral hyperperfusion following endarterectomy for unilateral cervical internal carotid artery stenosis. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:77–87
Stacy MR, Maxfield MW, Sinusas AJ (2012) Targeted molecular imaging of angiogenesis in PET and SPECT: a review. Yale J Biol Med 85:75–86
Gambhir SS, Czernin J, Schwimmer J, Silverman DH, Coleman RE, Phelps ME (2001) A tabulated summary of the FDG PET literature. J Nucl Med 42:1S–93S
Aparici CM, Carlson D, Nguyen N, Hawkins RA, Seo Y (2012) Combined SPECT and multidetector CT for prostate cancer evaluations. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:48–54
Eary JF, Hawkins DS, Rodler ET, Conrad EUI (2011) 18F-FDG PET in sarcoma treatment response imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 1:47–53
Gambhir SS (2002) Molecular imaging of cancer with positron emission tomography. Nat Rev Cancer 2:683–693
Grassi I, Nanni C, Allegri V, Morigi JJ, Montini GC, Castellucci P et al (2012) The clinical use of PET with 11C-acetate. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:33–47
Zhao R, Wang J, Deng J, Yang W, Wang J (2012) Efficacy of 99mTc-EDDA/HYNIC-TOC SPECT/CT scintigraphy in Graves’ ophthalmopathy. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:242–247
Cai W, Rao J, Gambhir SS, Chen X (2006) How molecular imaging is speeding up anti-angiogenic drug development. Mol Cancer Ther 5:2624–2633
Hao G, Hajibeigi A, De León-Rodríguez LM, Öz OK, Sun X (2011) Peptoid-based PET imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor receptor (VEGFR) expression. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 1:65–75
Wang RE, Niu Y, Wu H, Amin MN, Cai J (2011) Development of NGR peptide-based agents for tumor imaging. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 1:36–46
Zhang Y, Hong H, Engle JW, Yang Y, Barnhart TE, Cai W (2012) Positron emission tomography and near-infrared fluorescence imaging of vascular endothelial growth factor with dual-labeled bevacizumab. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:1–13
Ferrara N (2004) Vascular endothelial growth factor: basic science and clinical progress. Endocr Rev 25:581–611
Ferrara N (2002) VEGF and the quest for tumour angiogenesis factors. Nat Rev Cancer 2:795–803
Cai W, Niu G, Chen X (2008) Imaging of integrins as biomarkers for tumor angiogenesis. Curr Pharm Des 14:2943–2973
Almutairi A, Rossin R, Shokeen M, Hagooly A, Ananth A, Capoccia B et al (2009) Biodegradable dendritic positron-emitting nanoprobes for the noninvasive imaging of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:685–690
Jeong JM, Hong MK, Chang YS, Lee YS, Kim YJ, Cheon GJ et al (2008) Preparation of a promising angiogenesis PET imaging agent: 68Ga-labeled c(RGDyK)-isothiocyanatobenzyl-1,4,7-triazacyclononane-1,4,7-triacetic acid and feasibility studies in mice. J Nucl Med 49:830–836
Potter LR, Hunter T (2001) Guanylyl cyclase-linked natriuretic peptide receptors: structure and regulation. J Biol Chem 276:6057–6060
van den Akker F (2001) Structural insights into the ligand binding domains of membrane bound guanylyl cyclases and natriuretic peptide receptors. J Mol Biol 311:923–937
Liu Y, Pressly ED, Abendschein DR, Hawker CJ, Woodard GE, Woodard PK et al (2011) Targeting angiogenesis using a C-type atrial natriuretic factor-conjugated nanoprobe and PET. J Nucl Med 52:1956–1963
Cai W, Hong H (2011) Peptoid and positron emission tomography: an appealing combination. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 1:76–79
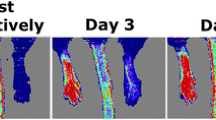
Willmann JK, Chen K, Wang H, Paulmurugan R, Rollins M, Cai W et al (2008) Monitoring of the biological response to murine hindlimb ischemia with 64Cu-labeled vascular endothelial growth factor-121 positron emission tomography. Circulation 117:915–922
Penuelas I, Aranguren XL, Abizanda G, Marti-Climent JM, Uriz M, Ecay M et al (2007) 13N-ammonia PET as a measurement of hindlimb perfusion in a mouse model of peripheral artery occlusive disease. J Nucl Med 48:1216–1223
Hua J, Dobrucki LW, Sadeghi MM, Zhang J, Bourke BN, Cavaliere P et al (2005) Noninvasive imaging of angiogenesis with a 99mTc-labeled peptide targeted at alphavbeta3 integrin after murine hindlimb ischemia. Circulation 111:3255–3260
Dobrucki LW, Dione DP, Kalinowski L, Dione D, Mendizabal M, Yu J et al (2009) Serial noninvasive targeted imaging of peripheral angiogenesis: validation and application of a semiautomated quantitative approach. J Nucl Med 50:1356–1363
Depairon M, De Landsheere C, Merlo P, Del Fiore G, Quaglia L, Peters JM et al (1988) Effect of exercise on the leg distribution of C15O2 and 15O2 in normals and in patients with peripheral ischemia: a study using positron tomography. Int Angiol 7:254–257
Depairon M, Depresseux JC, De Landsheere C, Merlo P, Del Fiore G, Quaglia L et al (1988) Regional blood flow and oxygen consumption in the leg muscles of normal subjects and in those with arterial insufficiency. Study of the distribution of C15O2 and of 15O2 using positron emission tomography. J Mal Vasc 13:107–115
Keenan GF, Ashcroft GP, Roditi GH, Hutchison JD, Evans NT, Mikecz P et al (1995) Measurement of lower limb blood flow in patients with neurogenic claudication using positron emission tomography. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20:408–411
Scremin OU, Figoni SF, Norman K, Scremin AM, Kunkel CF, Opava-Rutter D et al (2010) Preamputation evaluation of lower-limb skeletal muscle perfusion with H 152 O positron emission tomography. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 89:473–486
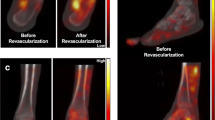
Nawaz A, Saboury B, Basu S, Zhuang H, Moghadam-Kia S, Werner T et al (2012) Relation between popliteal-tibial artery atherosclerosis and global glycolytic metabolism in the affected diabetic foot: a pilot study using quantitative FDG-PET. J Am Podiatr Med Assoc 102:240–246
Nolting DD, Nickels ML, Guo N, Pham W (2012) Molecular imaging probe development: a chemistry perspective. Am J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2:273–306
Beller GA, Sinusas AJ (1990) Experimental studies of the physiologic properties of technetium-99m isonitriles. Am J Cardiol 66:5E–8E
Bostrom PA, Diemer H, Leide S, Lilja B, Bergqvist D (1993) 99mTc-sestamibi uptake in the leg muscles and in the myocardium in patients with intermittent claudication. Angiology 44:971–976
Hamanaka D, Odori T, Maeda H, Ishii Y, Hayakawa K, Torizuka K (1984) A quantitative assessment of scintigraphy of the legs using 201Tl. Eur J Nucl Med 9:12–16
Kusmierek J, Dabrowski J, Bienkiewicz M, Szuminski R, Plachcinska A (2006) Radionuclide assessment of lower limb perfusion using 99mTc-MIBI in early stages of atherosclerosis. Nucl Med Rev Cent East Eur 9:18–23
Miles KA, Barber RW, Wraight EP, Cooper M, Appleton DS (1992) Leg muscle scintigraphy with 99mTc-MIBI in the assessment of peripheral vascular (arterial) disease. Nucl Med Commun 13:593–603
Forrest I, Hayes G, Smith A, Yip TC, Walker PM (1989) Identification of clinically significant skeletal muscle necrosis by single photon emission computed tomography. Can J Surg 32:109–112
Yip TC, Houle S, Tittley JG, Walker PM (1992) Quantification of skeletal muscle necrosis in the lower extremities using 99mTc pyrophosphate with single photon emission computed tomography. Nucl Med Commun 13:47–52
Bajnok L, Kozlovszky B, Varga J, Antalffy J, Olvaszto S, Fulop T Jr (1994) Technetium-99m sestamibi scintigraphy for the assessment of lower extremity ischaemia in peripheral arterial disease. Eur J Nucl Med 21:1326–1332
Dobrucki LW, Sinusas AJ (2010) PET and SPECT in cardiovascular molecular imaging. Nat Rev Cardiol 7:38–47
Wu AM (2009) Antibodies and antimatter: the resurgence of immuno-PET. J Nucl Med 50:2–5
Wu AM, Senter PD (2005) Arming antibodies: prospects and challenges for immunoconjugates. Nat Biotechnol 23:1137–1146
Zhang Y, Hong H, Engle JW, Yang Y, Theuer CP, Barnhart TE et al (2012) Positron emission tomography and optical imaging of tumor CD105 expression with a dual-labeled monoclonal antibody. Mol Pharm 9:645–653
Hong H, Severin GW, Yang Y, Engle JW, Zhang Y, Barnhart TE et al (2012) Positron emission tomography imaging of CD105 expression with 89Zr-Df-TRC105. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 39:138–148
Zhang Y, Hong H, Engle JW, Bean J, Yang Y, Leigh BR et al (2011) Positron emission tomography imaging of CD105 expression with a 64Cu-labeled monoclonal antibody: NOTA is superior to DOTA. PLoS One 6:e28005
Engle JW, Hong H, Zhang Y, Valdovinos HF, Myklejord DV, Barnhart TE et al (2012) Positron emission tomography imaging of tumor angiogenesis with a 66Ga-labeled monoclonal antibody. Mol Pharm 9:1441–1448
Dallas NA, Samuel S, Xia L, Fan F, Gray MJ, Lim SJ et al (2008) Endoglin (CD105): a marker of tumor vasculature and potential target for therapy. Clin Cancer Res 14:1931–1937
Zhang Y, Yang Y, Hong H, Cai W (2011) Multimodality molecular imaging of CD105 (Endoglin) expression. Int J Clin Exp Med 4:32–42
Helisch A, Wagner S, Khan N, Drinane M, Wolfram S, Heil M et al (2006) Impact of mouse strain differences in innate hindlimb collateral vasculature. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 26:520–526
Tirziu D, Moodie KL, Zhuang ZW, Singer K, Helisch A, Dunn JF et al (2005) Delayed arteriogenesis in hypercholesterolemic mice. Circulation 112:2501–2509
Saucy F, Dischl B, Delachaux A, Feihl F, Liaudet L, Waeber B et al (2006) Foot skin blood flow following infrainguinal revascularization for critical lower limb ischemia. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 31:401–406
Murohara T, Asahara T, Silver M, Bauters C, Masuda H, Kalka C et al (1998) Nitric oxide synthase modulates angiogenesis in response to tissue ischemia. J Clin Invest 101:2567–2578
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge financial support from the University of Wisconsin Carbone Cancer Center, the Department of Defense (W81XWH-11-1-0644), and the Elsa U. Pardee Foundation.
Conflict of interest
The authors have declared that no competing interest exists.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Orbay, H., Hong, H., Zhang, Y. et al. PET/SPECT imaging of hindlimb ischemia: focusing on angiogenesis and blood flow. Angiogenesis 16, 279–287 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9319-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-012-9319-4