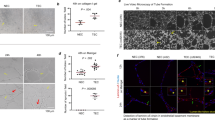
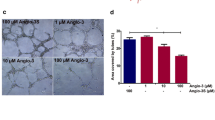
Abstract
Angiogenesis is important for tumor growth and metastasis. CLT1 (CGLIIQKNEC), a peptide that binds to tumor interstitial spaces in the presence of fibrin-fibronectin, has structural similarity to the anti-angiogenic β-sheet peptides anastellin and anginex. This similarity is reflected in the ability of CLT1 to form co-aggregates with fibronectin that induce an unfolded protein response and cause autophagic cell death in proliferating endothelial cells. CLT1 cytotoxicity is mediated at least in parts by a novel CLT1 binding protein, Chloride Intracellular Channel 1 (CLIC1), which promotes internalization of CLT1-fibronectin co-aggregates in a mechanism that depends on the LIIQK amino acid sequence of CLT1. LIIQK encompasses amino acid residues relevant for CLT1 binding to CLIC1 and in addition, facilitates the formation of CLT1-fibronectin co-aggregates, which in turn promote translocation of CLIC1 to the endothelial cell surface through ligation of integrin αvβ3. Paralleling the in vitro results, we found that CLT1 co-localizes with CLIC1 and fibronectin in angiogenic blood vessels in vivo, and that CLT1 treatment inhibited angiogenesis and tumor growth. Our findings show that CLT1 is a new anti-angiogenic compound, and its mechanism of action is to form co-aggregates with fibronectin, which bind to angiogenic endothelial cells through integrins, become internalized through CLIC1 and elicit a cytotoxic unfolded protein response. The simple structure and high potency of CLT1 make it a potentially useful compound for anti-angiogenic treatments.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hanahan D, Folkman J (1996) Patterns and emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis. Cell 86(3):353–364. doi:S0092-8674(00)80108-7
Neri D, Bicknell R (2005) Tumour vascular targeting. Nat Rev Cancer 5(6):436–446. doi:10.1038/nrc1627
Bergers G, Brekken R, McMahon G, Vu TH, Itoh T, Tamaki K, Tanzawa K, Thorpe P, Itohara S, Werb Z, Hanahan D (2000) Matrix metalloproteinase-9 triggers the angiogenic switch during carcinogenesis. Nat Cell Biol 2(10):737–744. doi:10.1038/35036374
Giancotti FG, Ruoslahti E (1999) Integrin signaling. Science 285(5430):1028–1032
Borgstrom P, Hillan KJ, Sriramarao P, Ferrara N (1996) Complete inhibition of angiogenesis and growth of microtumors by anti-vascular endothelial growth factor neutralizing antibody: novel concepts of angiostatic therapy from intravital videomicroscopy. Cancer Res 56(17):4032–4039
Burke PA, DeNardo SJ, Miers LA, Lamborn KR, Matzku S, DeNardo GL (2002) Cilengitide targeting of alpha(v)beta(3) integrin receptor synergizes with radioimmunotherapy to increase efficacy and apoptosis in breast cancer xenografts. Cancer Res 62(15):4263–4272
Schueneman AJ, Himmelfarb E, Geng L, Tan J, Donnelly E, Mendel D, McMahon G, Hallahan DE (2003) SU11248 maintenance therapy prevents tumor regrowth after fractionated irradiation of murine tumor models. Cancer Res 63(14):4009–4016
Wilhelm SM, Carter C, Tang L, Wilkie D, McNabola A, Rong H, Chen C, Zhang X, Vincent P, McHugh M, Cao Y, Shujath J, Gawlak S, Eveleigh D, Rowley B, Liu L, Adnane L, Lynch M, Auclair D, Taylor I, Gedrich R, Voznesensky A, Riedl B, Post LE, Bollag G, Trail PA (2004) BAY 43–9006 exhibits broad spectrum oral antitumor activity and targets the RAF/MEK/ERK pathway and receptor tyrosine kinases involved in tumor progression and angiogenesis. Cancer Res 64(19):7099–7109. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-1443
Faivre S, Demetri G, Sargent W, Raymond E (2007) Molecular basis for sunitinib efficacy and future clinical development. Nat Rev Drug Discov 6(9):734–745. doi:10.1038/nrd2380
Ivy SP, Wick JY, Kaufman BM (2009) An overview of small-molecule inhibitors of VEGFR signaling. Nat Rev Clin Oncol 6(10):569–579. doi:10.1038/nrclinonc.2009.130
Je Y, Schutz FA, Choueiri TK (2009) Risk of bleeding with vascular endothelial growth factor receptor tyrosine-kinase inhibitors sunitinib and sorafenib: a systematic review and meta-analysis of clinical trials. Lancet Oncol 10(10):967–974. doi:10.1016/S1470-2045(09)70222-0
O’Reilly MS, Pirie-Shepherd S, Lane WS, Folkman J (1999) Antiangiogenic activity of the cleaved conformation of the serpin antithrombin. Science 285(5435):1926–1928
O’Reilly MS, Boehm T, Shing Y, Fukai N, Vasios G, Lane WS, Flynn E, Birkhead JR, Olsen BR, Folkman J (1997) Endostatin: an endogenous inhibitor of angiogenesis and tumor growth. Cell 88(2):277–285. doi:S0092-8674(00)81848-6
Yi M, Sakai T, Fassler R, Ruoslahti E (2003) Antiangiogenic proteins require plasma fibronectin or vitronectin for in vivo activity. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(20):11435–11438. doi:10.1073/pnas.1635112100
Akerman ME, Pilch J, Peters D, Ruoslahti E (2005) Angiostatic peptides use plasma fibronectin to home to angiogenic vasculature. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(6):2040–2045. doi:10.1073/pnas.0409844102
Morla A, Zhang Z, Ruoslahti E (1994) Superfibronectin is a functionally distinct form of fibronectin. Nature 367(6459):193–196. doi:10.1038/367193a0
Briknarova K, Akerman ME, Hoyt DW, Ruoslahti E, Ely KR (2003) Anastellin, an FN3 fragment with fibronectin polymerization activity, resembles amyloid fibril precursors. J Mol Biol 332(1):205–215. doi:S0022283603008908
Hohenester E, Sasaki T, Olsen BR, Timpl R (1998) Crystal structure of the angiogenesis inhibitor endostatin at 1.5 A resolution. EMBO J 17(6):1656–1664. doi:10.1093/emboj/17.6.1656
Paris D, Townsend K, Quadros A, Humphrey J, Sun J, Brem S, Wotoczek-Obadia M, DelleDonne A, Patel N, Obregon DF, Crescentini R, Abdullah L, Coppola D, Rojiani AM, Crawford F, Sebti SM, Mullan M (2004) Inhibition of angiogenesis by Abeta peptides. Angiogenesis 7(1):75–85. doi:10.1023/B:AGEN.0000037335.17717.bf
Schreuder HA, de Boer B, Dijkema R, Mulders J, Theunissen HJ, Grootenhuis PD, Hol WG (1994) The intact and cleaved human antithrombin III complex as a model for serpin-proteinase interactions. Nat Struct Biol 1(1):48–54
Mayo KH, Dings RP, Flader C, Nesmelova I, Hargittai B, van der Schaft DW, van Eijk LI, Walek D, Haseman J, Hoye TR, Griffioen AW (2003) Design of a partial peptide mimetic of anginex with antiangiogenic and anticancer activity. J Biol Chem 278(46):45746–45752. doi:10.1074/jbc.M308608200
Hu X, Crick SL, Bu G, Frieden C, Pappu RV, Lee JM (2009) Amyloid seeds formed by cellular uptake, concentration, and aggregation of the amyloid-beta peptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106(48):20324–20329. doi:10.1073/pnas.0911281106
Pilch J, Franzin CM, Knowles LM, Ferrer FJ, Marassi FM, Ruoslahti E (2006) The anti-angiogenic peptide anginex disrupts the cell membrane. J Mol Biol 356(4):876–885. doi:10.1016/j.jmb.2005.12.006
Arap W, Pasqualini R, Ruoslahti E (1998) Cancer treatment by targeted drug delivery to tumor vasculature in a mouse model. Science 279(5349):377–380
Christian S, Pilch J, Akerman ME, Porkka K, Laakkonen P, Ruoslahti E (2003) Nucleolin expressed at the cell surface is a marker of endothelial cells in angiogenic blood vessels. J Cell Biol 163(4):871–878. doi:10.1083/jcb.200304132
Fogal V, Zhang L, Krajewski S, Ruoslahti E (2008) Mitochondrial/cell-surface protein p32/gC1qR as a molecular target in tumor cells and tumor stroma. Cancer Res 68(17):7210–7218. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-07-6752
Pilch J, Brown DM, Komatsu M, Jarvinen TA, Yang M, Peters D, Hoffman RM, Ruoslahti E (2006) Peptides selected for binding to clotted plasma accumulate in tumor stroma and wounds. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(8):2800–2804. doi:10.1073/pnas.0511219103
Knowles LM, Yang C, Osterman A, Smith JW (2008) Inhibition of fatty-acid synthase induces caspase-8-mediated tumor cell apoptosis by up-regulating DDIT4. J Biol Chem 283(46):31378–31384. doi:10.1074/jbc.M803384200
Hood BL, Grahovac J, Flint MS, Sun M, Charro N, Becker D, Wells A, Conrads TP (2010) Proteomic analysis of laser microdissected melanoma cells from skin organ cultures. J Proteome Res 9(7):3656–3663. doi:10.1021/pr100164x
Malik G, Knowles LM, Dhir R, Xu S, Yang S, Ruoslahti E, Pilch J (2010) Plasma fibronectin promotes lung metastasis by contributions to fibrin clots and tumor cell invasion. Cancer Res 70(11):4327–4334. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3312
Yi M, Ruoslahti E (2001) A fibronectin fragment inhibits tumor growth, angiogenesis, and metastasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 98(2):620–624. doi:10.1073/pnas.98.2.620
Goodchild SC, Howell MW, Littler DR, Mandyam RA, Sale KL, Mazzanti M, Breit SN, Curmi PM, Brown LJ (2010) Metamorphic response of the CLIC1 chloride intracellular ion channel protein upon membrane interaction. Biochemistry 49(25):5278–5289. doi:10.1021/bi100111c
Kranenburg O, Kroon-Batenburg LM, Reijerkerk A, Wu YP, Voest EE, Gebbink MF (2003) Recombinant endostatin forms amyloid fibrils that bind and are cytotoxic to murine neuroblastoma cells in vitro. FEBS Lett 539(1–3):149–155. doi:S0014579303002187
Menzies FM, Moreau K, Rubinsztein DC (2011) Protein misfolding disorders and macroautophagy. Curr Opin Cell Biol 23(2):190–197. doi:10.1016/j.ceb.2010.10.010
Kumar R, Yoneda J, Bucana CD, Fidler IJ (1998) Regulation of distinct steps of angiogenesis by different angiogenic molecules. Int J Oncol 12(4):749–757
Ellerby HM, Arap W, Ellerby LM, Kain R, Andrusiak R, Rio GD, Krajewski S, Lombardo CR, Rao R, Ruoslahti E, Bredesen DE, Pasqualini R (1999) Anti-cancer activity of targeted pro-apoptotic peptides. Nat Med 5(9):1032–1038
Hill JJ, Tremblay TL, Pen A, Li J, Robotham AC, Lenferink AE, Wang E, O’Connor-McCourt M, Kelly JF (2011) Identification of vascular breast tumor markers by laser capture microdissection and label-free LC-MS. J Proteome Res 10(5):2479–2493
Milton RH, Abeti R, Averaimo S, DeBiasi S, Vitellaro L, Jiang L, Curmi PM, Breit SN, Duchen MR, Mazzanti M (2008) CLIC1 function is required for beta-amyloid-induced generation of reactive oxygen species by microglia. J Neurosci 28(45):11488–11499. doi:10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2431-08.2008
Tung JJ, Kitajewski J (2010) Chloride intracellular channel 1 functions in endothelial cell growth and migration. J Angiogenes Res 2:23. doi:10.1186/2040-2384-2-23
Tung JJ, Hobert O, Berryman M, Kitajewski J (2009) Chloride intracellular channel 4 is involved in endothelial proliferation and morphogenesis in vitro. Angiogenesis 12(3):209–220. doi:10.1007/s10456-009-9139-3
Ruoslahti E (1984) Fibronectin in cell adhesion and invasion. Cancer Metastasis Rev 3(1):43–51
Magnussen A, Kasman IM, Norberg S, Baluk P, Murray R, McDonald DM (2005) Rapid access of antibodies to alpha5beta1 integrin overexpressed on the luminal surface of tumor blood vessels. Cancer Res 65(7):2712–2721. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2691
Yamamoto A, Tagawa Y, Yoshimori T, Moriyama Y, Masaki R, Tashiro Y (1998) Bafilomycin A1 prevents maturation of autophagic vacuoles by inhibiting fusion between autophagosomes and lysosomes in rat hepatoma cell line, H-4-II-E cells. Cell Struct Funct 23(1):33–42
Norambuena A, Schwartz MA (2011) Effects of integrin-mediated cell adhesion on plasma membrane lipid raft components and signaling. Mol Biol Cell 22(18):3456–3464. doi:10.1091/mbc.E11-04-0361
Gan B, Yoo Y, Guan JL (2006) Association of focal adhesion kinase with tuberous sclerosis complex 2 in the regulation of s6 kinase activation and cell growth. J Biol Chem 281(49):37321–37329. doi:10.1074/jbc.M605241200
Thijssen VL, Barkan B, Shoji H, Aries IM, Mathieu V, Deltour L, Hackeng TM, Kiss R, Kloog Y, Poirier F, Griffioen AW (2010) Tumor cells secrete galectin-1 to enhance endothelial cell activity. Cancer Res 70(15):6216–6224. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4150
Thijssen VL, Postel R, Brandwijk RJ, Dings RP, Nesmelova I, Satijn S, Verhofstad N, Nakabeppu Y, Baum LG, Bakkers J, Mayo KH, Poirier F, Griffioen AW (2006) Galectin-1 is essential in tumor angiogenesis and is a target for antiangiogenesis therapy. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103(43):15975–15980. doi:10.1073/pnas.0603883103
Belloni D, Veschini L, Foglieni C, Dell’Antonio G, Caligaris-Cappio F, Ferrarini M, Ferrero E (2010) Bortezomib induces autophagic death in proliferating human endothelial cells. Exp Cell Res 316(6):1010–1018. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2009.11.005
Nguyen TM, Subramanian IV, Kelekar A, Ramakrishnan S (2007) Kringle 5 of human plasminogen, an angiogenesis inhibitor, induces both autophagy and apoptotic death in endothelial cells. Blood 109(11):4793–4802. doi:10.1182/blood-2006-11-059352
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Erkki Ruoslahti for providing anastellin expression clones as well as for helpful discussions and comments on the manuscript. We also thank Dr. Per Basse, Dr. Simon Watkins and the UPCI Imaging Facility for help with confocal microscopy. This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants CA134330 (JP), P50 CA90386 (pilot project to JP) and P30CA047904 (UPCI CCSG), and Department of Defense grant PC073635-NIA (JP).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical standards
Experiments comply with current U.S. law.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Knowles, L.M., Malik, G., Hood, B.L. et al. CLT1 targets angiogenic endothelium through CLIC1 and fibronectin. Angiogenesis 15, 115–129 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9247-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9247-8