Abstract
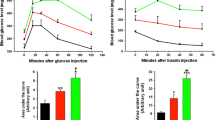
Obesity induces metabolic disorders such as type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases and has become a global health concern. Recent studies imply that fat accumulation in nonadipose tissue correlates with metabolic disorders. However, there are no suitable animal models to evaluate this phenomenon. This study investigated the characteristics of metabolic disorders found in cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus). Blood biochemical examinations revealed that cotton rats, predominantly males, developed hyperinsulinemia, hyperglycemia, and dyslipidemia when fed a normal diet. The islets increased in size through β-cell hyperplasia, which was associated with serum insulin level in both sexes, strongly indicating insulin resistance. In male cotton rats, oxidative stress was observed in β cells, and macrophage infiltration into the visceral white adipose tissue was reported, both of which were associated with serum insulin level without visceral obesity. In contrast, female cotton rats developed hyperinsulinemia without histopathological changes that were reported in males. Adipocytes were found to be accumulated in the pancreas but not in the liver of both sexes during aging. Pancreatic fat accumulation was associated with the serum insulin level only in females. Taken together, cotton rats developed metabolic disorders associated with visceral fat inflammation in the absence of obesity. In addition, pancreatic ectopic fat may also be related to the early stages of these conditions. Thus, the cotton rat may serve as a novel and useful model for metabolic disorders characterized by visceral adipose inflammation and ectopic fat accumulation in the pancreas without obesity.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Azazy AA, Chance ML, Devaney E (1997) A time-course study of circulating antigen and parasite-specific antibody in cotton rats infected with Leishmania donovani. Ann Trop Med Parasitol 91:153–162
Blanco JC, Boukhvalova MS, Perez DR, Vogel SN, Kajon A (2014) Modeling human respiratory viral infections in the cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus). J Antivir Antiretrovir 6:40–42
Bock T, Pakkenberg B, Buschard K (2003) Increased islet volume but unchanged islet number in ob/ob mice. Diabetes 52:1716–1722
Boutens L, Stienstra R (2016) Adipose tissue macrophages: going off track during obesity. Diabetologia 59:879–894
Catanzaro R, Cuffari B, Italia A, Marotta F (2016) Exploring the metabolic syndrome: nonalcoholic fatty pancreas disease. World J Gastroenterol 22:7660–7675
Dolenšek J, Rupnik MS, Stožer A (2015) Structural similarities and differences between the human and the mouse pancreas. Islets 7:e1024405
Faith RE, Montgomery CA, Durfee WJ, Aguilar-Cordova E, Wyde PR (1997) The cotton rat in biomedical research. Lab Anim Sci 47:337–345
Fraulob JC, Ogg-Diamantino R, Fernandes-Santos C, Aguila MB, Mandarim-de-Lacerda CA (2010) A mouse model of metabolic syndrome: insulin resistance, fatty liver and non-alcoholic fatty pancreas disease (NAFPD) in C57BL/6 mice fed a high fat diet. J Clin Biochem Nutr 46:212–223
Gu D, Sarvetnick N (1993) Epithelial cell proliferation and islet neogenesis in IFN-gamma transgenic mice. Development 118:33–46
Ichii O, Nakamura T, Irie T, Kouguchi H, Nakamura D, Nakamura S, Sato S, Yokoyama K, Horino T, Sunden Y, Elewa YH, Kon Y (2016) Female cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus) develop chronic anemia with renal inflammation and cystic changes. Histochem Cell Biol 146:351–362
Ichii O, Nakamura T, Irie T, Kouguchi H, Sotozaki K, Horino T, Sunden Y, Elewa YHA, Kon Y (2018) Close pathological correlations between chronic kidney disease and reproductive organ-associated abnormalities in female cotton rats. Exp Biol Med 243:418–427
Inada A, Nienaber C, Katsuta H, Fujitani Y, Levine J, Morita R, Sharma A, Bonner-Weir S (2008) Carbonic anhydrase II-positive pancreatic cells are progenitors for both endocrine and exocrine pancreas after birth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:19915–19919
Kanda Y, Shimoda M, Hamamoto S, Tawaramoto K, Kawasaki F, Hashiramoto M, Nakashima K, Matsuki M, Kaku K (2010) Molecular mechanism by which pioglitazone preserves pancreatic β-cells in obese diabetic mice: evidence for acute and chronic actions as a PPARγ agonist. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab 298:E278–E286
Kayamori F, Igarashi K (1994) Effects of dietary nasunin on the serum cholesterol level in rats. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem 58:570–571
Kooptiwut S, Wanchai K, Semprasert N, Srisawat C, Yenchitsomanus PT (2017) Estrogen attenuates AGTR1 expression to reduce pancreatic β-cell death from high glucose. Sci Rep 7:16639
Kroeze WK, Tanner CE (1985) Echinococcus multilocularis: responses to infection in cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). Int J Parasitol 15:233–238
Lanktree MB, Johansen CT, Joy TR, Hegele RA (2010) A translational view of the genetics of lipodystrophy and ectopic fat deposition. Prog Mol Biol Transl Sci 94:159–196
Lingvay I, Esser V, Legendre JL, Price AL, Wertz KM, Adams-Huet B, Zhang S, Unger RH, Szczepaniak LS (2009) Noninvasive quantification of pancreatic fat in humans. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 94:4070–4076
Matsuda A, Makino N, Tozawa T, Shirahata N, Honda T, Ikeda Y, Sato H, Ito M, Kakizaki Y, Akamatsu M, Ueno Y, Kawata S (2014) Pancreatic fat accumulation, fibrosis, and acinar cell injury in the Zucker diabetic fatty rat fed a chronic high-fat diet. Pancreas 43:735–743
Miao Z, Yan S, Wang J, Wang B, Li Y, Xing X, Yuan Y, Meng D, Wang L, Gu J, Zhang S, Li C, Wang CY (2009) Insulin resistance acts as an independent risk factor exacerbating high-purine diet induced renal injury and knee joint gouty lesions. Inflamm Res 58:659–668
Nakamura T, Ichii O, Irie T, Mizoguchi T, Shinohara A, Kouguchi H, Sunden Y, Otsuka-Kanazawa S, Elewa YHA, Koshimoto C, Nagasaki KI, Kon Y (2018) Cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus) possess pharyngeal pouch remnants originating from different primordia. Histol Histopathol 33:555–565
Niewiesk S, Prince G (2002) Diversifying animal models: the use of hispid cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus) in infectious diseases. Lab Anim 36:357–372
Nolte T, Brander-Weber P, Dangler C, Deschl U, Elwell MR, Greaves P, Hailey R, Leach MW, Pandiri AR, Rogers A, Shackelford CC, Spencer A, Tanaka T, Ward JM (2016) Nonproliferative and proliferative lesions of the gastrointestinal tract, pancreas and salivary glands of the rat and mouse. J Toxicol Pathol 29:1S–125S
Riant E, Waget A, Cogo H, Arnal JF, Burcelin R, Gourdy P (2009) Estrogens protect against high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and glucose intolerance in mice. Endocrinology 150:2109–2117
Sattar N, Gill JM (2014) Type 2 diabetes as a disease of ectopic fat? BMC Med 12:123
Tajima S, Horiuchi S (1989) Biological reference data book on experimental animals, 1st ed (Japanese). Soft Science, Tokyo
Tsuchitani M, Sato J, Kokoshima H (2016) A comparison of the anatomical structure of the pancreas in experimental animals. J Toxicol Pathol 29:147–154
Tushuizen ME, Bunck MC, Pouwels PJ, Bontemps S, Van Waesberghe JH, Schindhelm RK, Mari A, Heine RJ, Diamant M (2007) Pancreatic fat content and β-cell function in men with and without type 2 diabetes. Diabetes Care 30:2916–2921
Waldum HL, Rørvik H, Falkmer S, Kawase S (1999) Neuroendocrine (ECL cell) differentiation of spontaneous gastric carcinomas of cotton rats (Sigmodon hispidus). Lab Anim Sci 49:241–247
Wang MY, Grayburn P, Chen S, Ravazzola M, Orci L, Unger RH (2008) Adipogenic capacity and the susceptibility to type 2 diabetes and metabolic syndrome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:6139–6144
Wellen KE, Fucho R, Gregor MF, Furuhashi M, Morgan C, Lindstad T, Vaillancourt E, Gorgun CZ, Saatcioglu F, Hotamisligil GS (2007) Coordinated regulation of nutrient and inflammatory responses by STAMP2 is essential for metabolic homeostasis. Cell 129:537–548
Yao L, Herlea-Pana O, Heuser-Baker J, Chen Y, Barlic-Dicen J (2014) Roles of the chemokine system in development of obesity, insulin resistance, and cardiovascular disease. J Immunol Res 181450
Acknowledgements
We would like to acknowledge Daisuke Nakamura, Saori Nakamura, Shinobu Sato, and Keisuke Yokoyama in Sankyo Labo Service Corporation, Inc., Sapporo, Hokkaido, Japan, for their assistance in the animal experiments.
Funding
This work was partially supported by JSPS KAKENHI Grant Number JP18K0703708.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the ethical standards of Hokkaido Institute of Public Health (approval No. K27-03). This article does not contain any studies with human participants performed by any of the authors.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nakamura, T., Ichii, O., Irie, T. et al. Cotton rat (Sigmodon hispidus) develops metabolic disorders associated with visceral adipose inflammation and fatty pancreas without obesity. Cell Tissue Res 375, 483–492 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2908-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00441-018-2908-9