Abstract
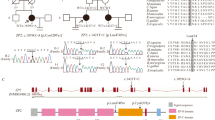
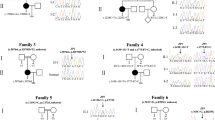
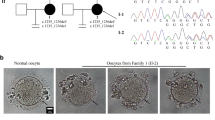
The zona pellucida (ZP) is an extracellular matrix universally surrounding mammalian eggs, which is essential for oogenesis, fertilization, and pre-implantation embryo development. Here, we identified two novel heritable mutations of ZP2 and ZP3, both occurring in an infertile female patient with ZP-abnormal eggs. Mouse models with the same mutations were generated by CRISPR/Cas9 gene editing system, and oocytes obtained from female mice with either single heterozygous mutation showed approximately half of the normal ZP thickness compared to wild-type oocytes. Importantly, oocytes with both heterozygous mutations showed a much thinner or even missing ZP that could not avoid polyspermy fertilization, following the patient’s pedigree. Further analysis confirmed that precursor proteins produced from either mutated ZP2 or ZP3 could not anchor to oocyte membranes. From these, we conclude that ZP mutations have dosage effects which can cause female infertility in humans. Finally, this patient was treated by intracytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) with an improved culture system and successfully delivered a healthy baby.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Avella MA, Baibakov B, Dean J (2014) A single domain of the ZP2 zona pellucida protein mediates gamete recognition in mice and humans. J Cell Biol 205:801–809. doi:10.1083/jcb.201404025
Bertrand E, Van den Bergh M, Englert Y (1996) Clinical parameters influencing human zona pellucida thickness. Fertil Steril 66:408–411
Conner SJ, Lefievre L, Hughes DC, Barratt CL (2005) Cracking the egg: increased complexity in the zona pellucida. Hum Reprod 20:1148–1152. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh835
Fagbohun CF, Downs SM (1990) Maturation of the mouse oocyte-cumulus cell complex: stimulation by lectins. Biol Reprod 42:413–423
Gook DA, Edgar DH, Borg J, Martic M (2008) Detection of zona pellucida proteins during human folliculogenesis. Hum Reprod 23:394–402. doi:10.1093/humrep/dem373
Gupta SK, Bhandari B, Shrestha A, Biswal BK, Palaniappan C, Malhotra SS, Gupta N (2012) Mammalian zona pellucida glycoproteins: structure and function during fertilization. Cell Tissue Res 349:665–678. doi:10.1007/s00441-011-1319-y
Gupta SK, Chakravarty S, Suraj K, Bansal P, Ganguly A, Jain MK, Bhandari B (2007) Structural and functional attributes of zona pellucida glycoproteins. Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl 63:203–216
Hasegawa A, Koyama K (2007) Contribution of zona proteins to oocyte growth. Soc Reprod Fertil Suppl 63:229–235
Hoodbhoy T, Aviles M, Baibakov B, Epifano O, Jimenez-Movilla M, Gauthier L, Dean J (2006) ZP2 and ZP3 traffic independently within oocytes prior to assembly into the extracellular zona pellucida. Mol Cell Biol 26:7991–7998. doi:10.1128/MCB.00904-06
Huang HL, Lv C, Zhao YC, Li W, He XM, Li P, Sha AG, Tian X, Papasian CJ, Deng HW, Lu GX, Xiao HM (2014) Mutant ZP1 in familial infertility. N Engl J Med 370:1220–1226. doi:10.1056/NEJMoa1308851
Jimenez-Movilla M, Dean J (2011) ZP2 and ZP3 cytoplasmic tails prevent premature interactions and ensure incorporation into the zona pellucida. J Cell Sci 124:940–950. doi:10.1242/jcs.079988
Jovine L, Qi H, Williams Z, Litscher E, Wassarman PM (2002) The ZP domain is a conserved module for polymerization of extracellular proteins. Nat Cell Biol 4:457–461. doi:10.1038/ncb802
Kiefer SM, Saling P (2002) Proteolytic processing of human zona pellucida proteins. Biol Reprod 66:407–414
Lefievre L, Conner SJ, Salpekar A, Olufowobi O, Ashton P, Pavlovic B, Lenton W, Afnan M, Brewis IA, Monk M, Hughes DC, Barratt CL (2004) Four zona pellucida glycoproteins are expressed in the human. Hum Reprod 19:1580–1586. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh301
Liu C, Litscher ES, Mortillo S, Sakai Y, Kinloch RA, Stewart CL, Wassarman PM (1996) Targeted disruption of the mZP3 gene results in production of eggs lacking a zona pellucida and infertility in female mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 93:5431–5436
Mannikko M, Tormala RM, Tuuri T, Haltia A, Martikainen H, Ala-Kokko L, Tapanainen JS, Lakkakorpi JT (2005) Association between sequence variations in genes encoding human zona pellucida glycoproteins and fertilization failure in IVF. Hum Reprod 20:1578–1585. doi:10.1093/humrep/deh837
Margalit M, Paz G, Yavetz H, Yogev L, Amit A, Hevlin-Schwartz T, Gupta SK, Kleiman SE (2012) Genetic and physiological study of morphologically abnormal human zona pellucida. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 165:70–76. doi:10.1016/j.ejogrb.2012.07.022
Matzuk MM, Burns KH, Viveiros MM, Eppig JJ (2002) Intercellular communication in the mammalian ovary: oocytes carry the conversation. Science 296:2178–2180. doi:10.1126/science.1071965
Pang PC, Chiu PC, Lee CL, Chang LY, Panico M, Morris HR, Haslam SM, Khoo KH, Clark GF, Yeung WS, Dell A (2011) Human sperm binding is mediated by the sialyl-Lewis(x) oligosaccharide on the zona pellucida. Science 333:1761–1764. doi:10.1126/science.1207438
Pokkyla RM, Lakkakorpi JT, Nuojua-Huttunen SH, Tapanainen JS (2011) Sequence variations in human ZP genes as potential modifiers of zona pellucida architecture. Fertil Steril 95:2669–2672. doi:10.1016/j.fertnstert.2011.01.168
Qi H, Williams Z, Wassarman PM (2002) Secretion and assembly of zona pellucida glycoproteins by growing mouse oocytes microinjected with epitope-tagged cDNAs for mZP2 and mZP3. Mol Biol Cell 13:530–541. doi:10.1091/mbc.01-09-0440
Rankin T, Familari M, Lee E, Ginsberg A, Dwyer N, Blanchette-Mackie J, Drago J, Westphal H, Dean J (1996) Mice homozygous for an insertional mutation in the Zp3 gene lack a zona pellucida and are infertile. Development 122:2903–2910
Rankin T, Talbot P, Lee E, Dean J (1999) Abnormal zonae pellucidae in mice lacking ZP1 result in early embryonic loss. Development 126:3847–3855
Rankin TL, O’Brien M, Lee E, Wigglesworth K, Eppig J, Dean J (2001) Defective zonae pellucidae in Zp2-null mice disrupt folliculogenesis, fertility and development. Development 128:1119–1126
Sauerbrun-Cutler MT, Vega M, Breborowicz A, Gonzales E, Stein D, Lederman M, Keltz M (2015) Oocyte zona pellucida dysmorphology is associated with diminished in vitro fertilization success. J Ovar Res 8:5. doi:10.1186/s13048-014-0111-5
Wassarman PM (2008) Zona pellucida glycoproteins. J Biol Chem 283:24285–24289. doi:10.1074/jbc.R800027200
Wassarman PM, Litscher ES (2012) Influence of the zona pellucida of the mouse egg on folliculogenesis and fertility. Int J Dev Biol 56:833–839. doi:10.1387/ijdb.120136pw
Wassarman PM, Litscher ES (2008) Mammalian fertilization: the egg’s multifunctional zona pellucida. Int J Dev Biol 52:665–676. doi:10.1387/ijdb.072524pw
Wassarman PM, Jovine L, Litscher ES (2001) A profile of fertilization in mammals. Nat Cell Biol 3:E59–E64. doi:10.1038/35055178
Wassarman PM, Jovine L, Litscher ES (2004) Mouse zona pellucida genes and glycoproteins. Cytogenet Genome Res 105:228–234. doi:10.1159/000078193
Wassarman PM, Qi H, Litscher ES (1997) Mutant female mice carrying a single mZP3 allele produce eggs with a thin zona pellucida, but reproduce normally. Proc Biol Sci 264:323–328. doi:10.1098/rspb.1997.0046
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank the participant and families for their contribution to this study. We are grateful to our colleagues in the laboratory for their assistance with the experiments and in the preparation of this manuscript. We thank Dr. Jun Xiong for discussions about the in vitro experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no conflict of interests.
Funding
This project was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81630035, 31401247, 31501196, 31471392, 31601177, 31401266, 31501197, 31501183, 81671521, and 31430056), the Ministry of Science and Technology of China (Grants 2016YFA0100400, 2015CB964800, 2014CB964601, and 2015CB964503), Shanghai Natural Science Foundation (Grant 16ZR1427200), Shanghai Rising-Star Program (17QA1402700), the Municipal Education Commission of Shanghai (16CG17 and 16CG19) and the Program for Young Excellent Talents in Tongji University (Grants 2000219115, 2000219117, and 1515219023).
Additional information
Wenqiang Liu, Kunming Li, Dandan Bai, and Jiqing Yin are contributed equally to this work.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, W., Li, K., Bai, D. et al. Dosage effects of ZP2 and ZP3 heterozygous mutations cause human infertility. Hum Genet 136, 975–985 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1822-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-017-1822-7