Abstract
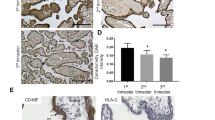
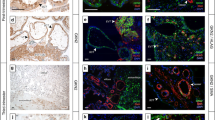
Normal placenta development relies on the ability of trophoblast cells to invade into the uterus and to build up an extensively vascularized feto-maternal tissue, necessary for the nutrition of the embryo. The ability of cell migration, invasion, and the ability to induce neovascularization are likewise hallmarks of cancer cells. The metastasis-associated genes MTA1 and MTA3 are known to be involved in cancer cell migration by regulation of cell adhesion proteins and to induce the expression of neoangiogenic cytokines, as recently shown by us for ovarian cancer cells. Therefore, we analyzed the expression of MTA1 and MTA3 in normal human placenta tissues and the chorionic cancer cell lines BeWo, JEG, and JAR. Immunohistochemical analysis revealed a rather strong expression of MTA1 and MTA3 in the nuclei of human trophoblast cells. A high expression level of MTA1 and MTA3 was further observed in the nuclei of human chorionic carcinoma cells, as shown by immunofluorescence analysis, and confirmed by Western blot and RT-PCR analysis. We conclude that the high expression level of MTA proteins in human chorionic cells might facilitate trophoblast cell migration and neoangiogenesis, and might further predispose human chorionic cancer cells with properties that are characteristic for this highly aggressive and metastatic carcinoma type.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Becker KF, Rosivatz E, Blechschmidt K, Kremmer E, Sarbia M, Höfler H (2007) Analysis of the E-cadherin repressor snail in primary human cancers. Cells Tissues Organs 185:204–212
Blechschmidt K, Kremmer E, Hollweck R, Mylonas I, Hofler H, Kremer M, Becker KF (2007a) The E-cadherin repressor snail plays a role in tumor progression of endometrioid adenocarcinomas. Diagn Mol Pathol 16:222–228
Blechschmidt K, Mylonas I, Mayr D, Schiessl B, Schulze S, Becker KF, Jeschke U (2007b) Expression of E-cadherin and its repressor snail in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic and HELLP pregnancies. Virchows Arch 450:195–202
Blechschmidt K, Sassen S, Schmalfeldt B, Schuster T, Hofler H, Becker KF (2008) The E-cadherin repressor snail is associated with lower overall survival of ovarian cancer patients. Br J Cancer 98:489–495
Burrows TD, King A, Loke YW (1996) Trophoblast migration during human placental implantation. Hum Reprod Update 2:307–321
Castro Alves C, Rosivatz E, Schott C, Hollweck R, Becker I, Sarbia M, Carneiro F, Becker KF (2007) Slug is overexpressed in gastric carcinomas and may act synergistically with SIP1 and Snail in the down-regulation of E-cadherin. J Pathol 211:507–515
Dannenmann C, Shabani N, Friese K, Jeschke U, Mylonas I, Bruning A (2008) The metastasis-associated gene MTA1 is upregulated in advanced ovarian cancer, represses ERbeta, and enhances expression of oncogenic cytokine GRO. Cancer Biol Ther 7:1460–1467
Fujita N, Jaye DL, Kajita M, Geigerman C, Moreno CS, Wade PA (2003) MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell 113:207–219
Hanahan D, Weinberg RA (2000) The hallmarks of cancer. Cell 100:57–70
Hugo H, Ackland ML, Blick T, Lawrence MG, Clements JA, Williams ED, Thompson EW (2007) Epithelial–mesenchymal and mesenchymal–epithelial transitions in carcinoma progression. J Cell Physiol 213:374–383
Keeley EC, Mehrad B, Strieter RM (2008) Chemokines as mediators of neovascularization. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 28:1928–1936
Manavathi B, Singh K, Kumar R (2007) MTA family of coregulators in nuclear receptor biology and pathology. Nucl Recept Signal 5:e010
Mendelson CR, Kamat A (2007) Mechanisms in the regulation of aromatase in developing ovary and placenta. J Steroid Biochem Mol Biol 106:62–70
Moustakas A, Heldin CH (2007) Signaling networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci 98:1512–1520
Mylonas I, Speer R, Makovitzky J, Richter DU, Briese V, Jeschke U, Friese K (2000) Immunohistochemical analysis of steroid receptors and glycodelin A (PP14) in isolated glandular epithelial cells of normal human endometrium. Histochem Cell Biol 114:405–411
Mylonas I, Schiessl B, Jeschke U, Vogl J, Makrigiannakis A, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Schulze S, Kainer F, Friese K (2006a) Expression of inhibin/activin subunits alpha (-alpha), beta A (-beta (A)) and beta B (-beta (B)) in placental tissue of normal and intrauterine growth restricted (IUGR) pregnancies. J Mol Histol 37:43–52
Mylonas I, Schiessl B, Jeschke U, Vogl J, Makrigiannakis A, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kainer F, Friese K (2006b) Expression of inhibin/activin subunits alpha (-alpha), betaA (-betaA), and betaB (-betaB) in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic, and HELLP pregnancies. Endocr Pathol 17:19–33
Mylonas I, Jeschke U, Shabani N, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Dian D, Friedl C, Kupka MS, Friese K (2007) Steroid receptors ERalpha, ERbeta, PR-A and PR-B are differentially expressed in normal and atrophic human endometrium. Histol Histopathol 22:169–176
Red-Horse K, Zhou Y, Genbacev O, Prakobphol A, Foulk R, McMaster M, Fisher SJ (2004) Trophoblast differentiation during embryo implantation and formation of the maternal-fetal interface. J Clin Invest 114:744–754
Schiessl B, Mylonas I, Hantschmann P, Kuhn C, Schulze S, Kunze S, Friese K, Jeschke U (2005) Expression of endothelial NO synthase, inducible NO synthase, and estrogen receptors alpha and beta in placental tissue of normal, preeclamptic, and intrauterine growth-restricted pregnancies. J Histochem Cytochem 53:1441–1449
Schiessl B, Mylonas I, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Schulze S, Friese K, Jeschke U (2006) Expression of estrogen receptor-alpha, estrogen receptor-beta and placental endothelial and inducible NO synthase in intrauterine growth-restricted and normal placentals. Arch Med Res 37:967–975
Shabani N, Kuhn C, Kunze S, Schulze S, Mayr D, Dian D, Gingelmaier A, Schindlbeck C, Willgeroth F, Sommer H, Jeschke U, Friese K, Mylonas I (2007) Prognostic significance of oestrogen receptor alpha (ERalpha) and beta (ERbeta), progesterone receptor A (PR-A) and B (PR-B) in endometrial carcinomas. Eur J Cancer 43:2434–2444
Vicovac L, Aplin JD (1996) Epithelial-mesenchymal transition during trophoblast differentiation. Acta Anat (Basel) 156:202–216
Yao YL, Yang WM (2003) The metastasis-associated proteins 1 and 2 form distinct protein complexes with histone deacetylase activity. J Biol Chem 278:42560–42568
Acknowledgments
We thank Susanne Kunze for excellent help in immunohistochemical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Brüning, A., Makovitzky, J., Gingelmaier, A. et al. The metastasis-associated genes MTA1 and MTA3 are abundantly expressed in human placenta and chorionic carcinoma cells. Histochem Cell Biol 132, 33–38 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0595-z
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00418-009-0595-z