Abstract
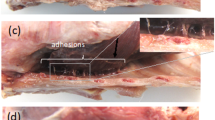
This study evaluated submicroscopic features of active pleural remodeling associated with chemical pleurodesis. Twenty seven rabbits received intrapleural injection of 0.5% silver nitrate (SN; N = 9) or 400 mg/kg talc slurry (N = 9) in 2 ml of saline solution; control rabbits (N = 9) received 2 ml of saline alone. The rabbits were sacrificed 15 minutes, 24 hours, or 7 days postinjection, and specimens of visceral pleura were obtained, fixed, and photographed for submicroscopic analysis. After 15 minutes of talc or SN exposure, prominent injury to the mesothelial cells and mesothelial cell–mesothelial basement membrane (MC–MBM) union was visible. There was focal remesothelialization of the denuded area through mesothelial cell migration, proliferation, and differentiation. After 24 hours, early wound healing, characterized by a superficial exudate, was evident where myofibroblasts had proliferated through a gap in the MC–MBM. After 7 days, proliferation of highly active myofibroblasts was observed; these cells produced abundant extracellular matrix components in a more organized distribution paralleling the surface. This third stage of remodeling was more evident with SN than talc-induced chemical pleurodesis. Our results suggest that ideal chemical pleurodesis results from injury to the MC–MBM union and abnormal wound healing, involving three essential steps: remesothelialization, fibroblastic proliferation, and extracellular matrix accumulation and remodeling.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
DAM Albuquerque VR Seidl VCT Santos JA Oliveira–Neto VL Capelozzi PRM Rocco WA Zin (2002) ArticleTitleThe effect of experimental pleurodesis caused by aluminum hydroxide on lung and chest wall mechanics Lung 179 293–303 Occurrence Handle10.1007/s004080000069
PM Andrews KR Porter (1973) ArticleTitleThe ultrastructural morphology and possible functional significance of mesothelial microvilli Anat Rec 177 409–426 Occurrence Handle10.1002/ar.1091770307 Occurrence Handle4127780
VL Capelozzi PHN Saldiva L Antonangelo TS Carvalho A Logulo CRR Carvalho D Deheinzelin (1997) ArticleTitleQuantitation in inflammatory pleural disease could be useful to distinguish tuberculous and paramalignant from chronic non-specific pleuritis J Clin Pathol 50 935–940 Occurrence Handle9462244
SR Dryzer J Joseph M Baumann K Birmingham AS Sahn C Strange (1993) ArticleTitleEarly inflammatory response of minocycline and tetracycline on the rabbit pleura Chest 104 1585–1588 Occurrence Handle8222827
SR Dryzer RW Light NS Wang CSH Sassoon SE Gruer FS Vargas (1994) ArticleTitleComparison of effectiveness of tetracycline and minocycline as pleural sclerosing agents in rabbits Chest 106 577–582 Occurrence Handle7774340
Y Fukuda M Ishizaki S Kudoh M Kitaichi N Yamanaka (1998) ArticleTitleLocalization of matrix metalloproteinases-1, -2, and -9 and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinase-2 in interstitial lung diseases Lab Invest 78 687–698 Occurrence Handle9645759
M Kasper G Haroske (1996) ArticleTitleAlterations in the alveolar epithelium after injury leading to pulmonary fibrosis Histol Histopathol 11 463–483 Occurrence Handle8861769
AL Katzeinstein JL Myers (1998) ArticleTitleIdiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clinical relevance of pathologic classification Am J Respir Crit Care Med 157 1301–1315 Occurrence Handle9563754
L Kennedy V Rusch C Strange RJ Ginsberg SA Sahn (1994) ArticleTitlePleurodesis using talc slurry Chest 106 342–346 Occurrence Handle7774299
C Kuhn Suffix3rd J Boldt TE King SuffixJr E Crouch T Vartio JA McDonald (1989) ArticleTitleAn immunohistochemical study of architectural remodeling and connective tissue synthesis in pulmonary fibrosis Am Rev Respir Dis 140 1693–1703 Occurrence Handle2604297
C Kuhn Suffix3rd JA McDonald (1991) ArticleTitleThe roles of the myofibroblasts in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: ultrastructural and immunohistochemical features of sites of active extracellular matrix synthesis Am J Pathol 138 1257–1265 Occurrence Handle2024710
BC Marshall A Santana QP Xu MJ Petersen EJ Campbell JR Hoidal HG Welgus (1993) ArticleTitleMetalloproteinases and tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases in mesothelial cells—cellular differentiation influences expression J Clin Invest 91 1792–1799 Occurrence Handle8386195
KN Michailova (1997) ArticleTitleUltrastructural observations on the human visceral pleura Eur J Morphol 35 125–135 Occurrence Handle10.1076/ejom.35.2.125.13063 Occurrence Handle9253590
SI Rennard M-C Jaurand J Bignon O Kawanami VJ Ferrans J Davidson R Crystal (1984) ArticleTitleRole of pleural mesothelial cells in the production of submesothelial connective tissue matrix of lung Am Rev Respir Dis 130 267–274 Occurrence Handle6465680
SA Sahn JT Good SuffixJr (1981) ArticleTitleThe effect of common sclerosing agents on the rabbit pleural space Am Rev Respir Dis 124 65–67 Occurrence Handle6167181
FS Vargas NS Wang HM Lee SE Gruer CSH Sassoon RW Light (1993) ArticleTitleEffectiveness of bleomycin in comparison to tetracycline as pleural sclerosing agent in rabbits Chest 104 1582–1584 Occurrence Handle7693399
FS Vargas LR Teixeira LMMF Silva AO Carmo RW Light (1995) ArticleTitleComparison of silver nitrate and tetracycline as pleural sclerosing agents in rabbits Chest 108 1080–1083 Occurrence Handle7555123
FS Vargas LR Teixeira MAC Vaz AO Carmo E Marchi PM Cury RW Light (2000) ArticleTitleSilver nitrate is superior to talc slurry in producing pleurodesis in rabbits Chest 118 808–813 Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.118.3.808 Occurrence Handle10988206
FS Vargas L Antonangelo V Capelozzi MAC Vaz EH Genofre E Marchi LR Teixeira (2002) ArticleTitleLung damage in experimental pleurodesis induced by silver nitrate or talc. One-year follow-up Chest 122 2122–2126 Occurrence Handle10.1378/chest.122.6.2122 Occurrence Handle12475856
NS Wang (1998) ArticleTitleAnatomy of the pleura Clin Chest Med 19 229–240 Occurrence Handle10.1016/S0272-5231(05)70074-5 Occurrence Handle9646978
U Wied K Andersen A Schultz E Rasmussen S Watt–Boolsen (1981) ArticleTitleSilver nitrate pleurodesis in spontaneous pneumothorax Scand J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 15 305–307 Occurrence Handle6753138
C Xie LR Teixeira JP McGovern RW Light (1998) ArticleTitleEffect of pneumothorax on pleurodesis induced with talc in rabbits Chest 114 1143–1146 Occurrence Handle9792590
PD Yurchenco JG Schittny (1990) ArticleTitleMolecular architecture of basement membrane FASEB J 4 1577–1590 Occurrence Handle2180767
PW Zimmer M Hill K Casey E Harvey DE Low (1997) ArticleTitleProspective randomized trial of talc slurry vs. bleomycin in pleurodesis for symptomatic malignant pleural effusions Chest 112 430–434 Occurrence Handle9266880
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Foundation to Support Research from the State of São Paulo (FAPESP), National Board of Scientific and Technologic Development (CNPq), and the Laboratories for Medical Research [LIM 5 and 29] FMUSP.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Genofre, E.H., Vargas, F.S., Antonangelo, L. et al. Ultrastructural Acute Features of Active Remodeling After Chemical Pleurodesis Induced by Silver Nitrate or Talc. Lung 183, 197–207 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-004-2536-x
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00408-004-2536-x