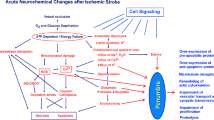
Abstract
Apoptotic cell death contributes to neuronal loss in the penumbral region of brain infarction. Activated caspase-3 (ACA-3) cleaves proteins including poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1 (PARP-1) important in DNA repair, thus promoting apoptosis. Overactivation of PARP-1 depletes NAD+ and ATP, resulting in necrosis. These cell death phenomena have been investigated mostly in experimental animals. We studied an autopsy cohort of 13 fatal ischemic stroke cases (symptoms 15 h to 18 days) and 2 controls by immunohistochemical techniques. The number of PARP-1 immunoreactive neurons was highest in the periinfarct area. Nuclear PARP-1 correlated with increasing neuronal necrosis (P = 0.013). Cytoplasmic PARP-1 correlated with TUNEL in periinfarct and core areas (P = 0.01). Cytoplasmic cleaved PARP-1 was inversely correlated with increasing necrotic damage (P = 0.001). PAR-polymers were detected in neurons confirming enzymatic activity of PARP-1. Cytoplasmic ACA-3 correlated with death receptor Fas (r s = 0.48; P = 0.005). In conclusion, the confirmation of the same pathways of cell death than previously described in experimental animal models encourages neuroprotective treatments acting on these mediators also in human stroke.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ACA:
-
Activated caspase-3
- AIF:
-
Apoptosis inducing factor
- PARP-1:
-
Poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase-1
- TUNEL:
-
Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT)-mediated dUTP nick end labeling
References
Andrabi SA, Kim NS, Yu S et al (2006) Poly(ADP-ribose) (PAR) polymer is a death signal. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 103:18308–18318
Ang BT, Yap E, Lim J et al (2003) Poly(adenosine diphosphate-ribose) polymerase expression in human traumatic brain injury. J Neurosurg 99:125–130
Chiarugi A (2005) Poly(ADP-ribosyl)ation and stroke. Pharmacol Res 52:15–24
Chu X, Fu X, Zou L et al (2007) Oncosis, the possible cell death pathway in astrocytes after focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res 1149:157–164
Cookson MR, Ince PG, Usher PA, Shaw PJ (1999) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase is found in both the nucleus and cytoplasm of human CNS neurons. Brain Res 834(1–2):182–185
del Zoppo GJ (2006) Stroke and neurovascular protection. N Engl J Med 354(6):553–555
Desnoyers S, Kaufmann SH, Poirier GG (1996) Alteration of the nucleolar localization of poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase upon treatment with transcription inhibitors. Exp Cell Res 227:146–153
Donnan GA (2008) The 2007 Feinberg lecture. A new road map for neuroprotection. Stroke 39:242–248
Durukan A, Tatlisumak T (2007) Acute ischemic stroke: overview of major experimental rodent models, pathophysiology, and therapy of focal cerebral ischemia. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 87:179–197
Eke A, Conger KA, Anderson M, Garcia JH (1990) Histologic assessment of neurons in rat models of cerebral ischemia. Stroke 21:299–304
Faden AI, Stoica B (2007) Neuroprotection: challenges and opportunities. Arch Neurol 64(6):794–800
Fakan S, Leduc Y, Lamarre D, Brunet G, Poirier GG (1988) Immunoelectron microscopical distribution of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase in the mammalian cell nucleus. Exp Cell Res 179(2):517–526
Ferrer I, Planas AM (2003) Signaling of cell death and cell survival following focal cerebral ischemia: life and death struggle in the penumbra. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol 62(4):329–339
Fisher M, Davalos A, Rogalewski A, Schneider A, Ringelstein EB, Schäbitz W (2006) Toward a multimodal neuroprotective treatment of stroke. Stroke 37:1129–1136
Graziani G, Battaini F, Zhang J (2005) PARP-1 inhibition to treat cancer, ischemia, inflammation. Pharmacol Res 52:1–4
Graziani G, Szabo C (2005) Clinical perspectives of PARP inhibitors. Pharmacol Res 52:109–118
Guglielmo MA, Chan PT, Cortez S et al (1998) The temporal profile and morphological features of neuronal death in human stroke resemble those observed in experimental forebrain ischemia: the potential role of apoptosis. Neurol Res 20(4):283–296
Ha HC, Snyder SH (2000) Poly(ADP-ribose) Polymerase-1 in the nervous system. Neurobiol Dis 7:225–239
Koh DW, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2005) Mediation of cell death by poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase-1. Pharmacol Res 52(1):5–14
Love S, Barber R, Srinivasan A, Wilcock GK (2000) Activation of caspase-3 in permanent and transient brain ischemia in man. NeuroReport 11:2495–2499
Love S, Barber R, Wilcock GK (2000) Neuronal death in brain infarcts in man. Neuropath Appl Neurobiol 26:55–66
McLaughlin B (2004) The kinder side of killer proteases: caspase activation contributes to neuroprotection and CNS remodeling. Apoptosis 9(2):111–121
Meder VS, Boeglin M, de Murcia G, Schreiber V (2005) PARP-1 and PARP-2 interact with nucleophosmin/B23 and accumulate in transcriptionally active nucleoli. J Cell Sci 118(1):211–222
Mehta SL, Manhas N, Raghubir R (2007) Molecular targets in cerebral ischemia for developing novel therapeutics. Brain Res Rev 54:34–66
Meli E, Pangallo M, Baronti R et al (2003) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase as a key player in excitotoxicity and post-ischemic brain damage. Toxicol Lett 139:153–162
Mitsios N, Gaffney J, Krupinski J et al (2007) Expression of signaling molecules associated with apoptosis in human stroke tissue. Cell Biochem Biophys 47(1):73–86
Moroni F (2007) Poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase 1 (PARP-1) and postischemic brain damage. Curr Opin Pharmacol 7:1–8
Pacher P, Szabo C (2008) Role of the peroxynitrite-poly(ADP-Ribose) polymerase pathway in human disease. Am J Pathol 173(1):2–13
Rami A, Bechmann I, Stehle JH (2008) Exploiting endogenous anti-apoptotic proteins for novel therapeutic strategies in cerebral ischemia. Prog Neurobiol 85(3):273–296
Sairanen T, Karjalainen-Lindsberg M, Paetau A, Ijäs P, Lindsberg PJ (2006) Apoptosis dominant in the periinfarct area of human ischemic stroke—a possible target of antiapoptotic treatments. Brain 129:189–199
Solaroglu I, Tsubokawa T, Cahill J, Zhang JH (2006) Anti-apoptotic effect of granulocyte-colony stimulating factor after focal cerebral ischemia in the rat. Neuroscience 143(4):965–974
Soldani C, Lazzè MC, Bottone MG et al (2001) Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase cleavage during apoptosis: when and where? Exp Cell Res 269(2):193–201
Stadelmann D, Mews I, Srinivasan A, Deckwerth TL, Lassmann H, Bruck W (2001) Expression of cell death-associated proteins in neuronal apoptosis associated with pontosubicular neuron necrosis. Brain Pathol 11(3):273–281
Szabo C, Pacher P, Swanson RA (2006) Novel modulators of poly(ADP-ribose)polymerase. Trends Pharmacol Sci 27:626–630
Velier JJ, Ellison JA, Kikly KK, Spera PA, Barone FC, Feuerstein GZ (1999) Caspase-8 and caspase-3 are expressed by different populations of cortical neurons undergoing delayed cell death after focal stroke in the rat. J Neurosci 19(14):5932–5941
Yu S, Wang H, Poitras MF et al (2002) Mediation of Poly(ADP-Ribose) Polymerase-1-dependent cell death by apoptosis-inducing factor. Science 297
Acknowledgments
The study was financially supported by The Finnish Academy, Sigrid Jusélius Foundation, HUCH governmental subsidiary grants for research (EVO), Päivikki and Sakari Sohlberg Foundation, H. Lundbeck Inc., Maire Taponen Foundation, The Finnish Medical Foundation, Finnish Cultural Foundation and Aarne Koskelo Foundation. The authors thank Ms. Tanja Eriksson and Mrs. Taru Puhakka for skillful technical assistance. This study belongs to a series of post-mortem stroke studies designated collectively as the Helsinki Stroke Study (HSS).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
T. Sairanen and R. Szepesi contributed equally to this study.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sairanen, T., Szepesi, R., Karjalainen-Lindsberg, ML. et al. Neuronal caspase-3 and PARP-1 correlate differentially with apoptosis and necrosis in ischemic human stroke. Acta Neuropathol 118, 541–552 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0559-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00401-009-0559-3