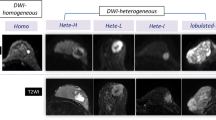
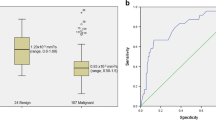
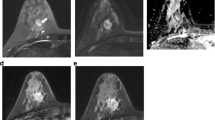
Abstract
Objectives
To determine the MRI features of triple-negative invasive breast cancer (TNBC) on dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging (DCE-MRI) and diffusion-weighted MR imaging (DWI) in comparison with ER-positive/HER2-negative (ER+) and HER2-positive cancer (HER2+).
Methods
A total of 271 invasive cancers in 269 patients undergoing preoperative MRI and surgery were included. Two radiologists retrospectively assessed morphological and kinetic characteristics on DCE-MRI and tumour detectability on DWI. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of lesions were measured. Clinical and MRI features of the three subtypes were compared.
Results
Compared with ER+ (n = 119) and HER2+ (n = 94), larger size, round/oval mass shape, smooth mass margin, and rim enhancement on DCE-MRI were significantly associated with TNBC (n = 58; P < 0.0001). On DWI, mean ADC value (×10−3 mm2/s) of TNBC (1.03) was higher than the mean ADC values for ER+ and HER2+ (0.89 and 0.84; P < 0.0001). There was no difference in tumour detectability (P = 0.099). Tumour size (P = 0.009), mass margin (smooth, P < 0.0001; irregular, P = 0.020), and ADC values (P = 0.002) on DCE-MRI and DWI were independent features of TNBC.
Conclusions
In addition to the morphological features, higher ADC values on DWI were independently associated with TNBC and could be useful in differentiating TNBC from ER+ and HER2+.
Key Points
• Triple-negative breast cancers (TNBC) lack oestrogen/progesterone receptors and HER2 expression/amplification.
• TNBCs are larger, better defined and more necrotic than conventional cancers.
• On MRI, necrosis yields high T2-weighted signal intensity and ADCs.
• High ADC values can be useful in diagnosing TNBC.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yamamoto Y, Iwase H (2010) Clinicopathological features and treatment strategy for triple-negative breast cancer. Int J Clin Oncol 15:341–351
de Ronde JJ, Hannemann J, Halfwerk H et al (2010) Concordance of clinical and molecular breast cancer subtyping in the context of preoperative chemotherapy response. Breast Cancer Res Treat 119:119–126
Denley H, Pinder SE, Elston CW, Lee AH, Ellis IO (2001) Preoperative assessment of prognostic factors in breast cancer. J Clin Pathol 54:20–24
Montagna E, Bagnardi V, Rotmensz N et al (2011) Immunohistochemically defined subtypes and outcome in occult breast carcinoma with axillary presentation. Breast Cancer Res Treat 129:867–875
Sorlie T, Perou CM, Tibshirani R et al (2001) Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 98:10869–10874
Perou CM, Sorlie T, Eisen MB et al (2000) Molecular portraits of human breast tumours. Nature 406:747–752
Li SP, Padhani AR, Taylor NJ et al (2011) Vascular characterisation of triple negative breast carcinomas using dynamic MRI. Eur Radiol 21:1364–1373
van de Vijver MJ, He YD, van’t Veer LJ et al (2002) A gene-expression signature as a predictor of survival in breast cancer. N Engl J Med 347:1999–2009
Desmedt C, Haibe-Kains B, Wirapati P et al (2008) Biological processes associated with breast cancer clinical outcome depend on the molecular subtypes. Clin Cancer Res 14:5158–5165
Sanchez-Munoz A, Garcia-Tapiador AM, Martinez-Ortega E et al (2008) Tumour molecular subtyping according to hormone receptors and HER2 status defines different pathological complete response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with locally advanced breast cancer. Clin Transl Oncol 10:646–653
Elsawaf Z, Sinn HP (2011) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical and histological correlations. Breast Care (Basel) 6:273–278
Ko ES, Lee BH, Kim HA, Noh WC, Kim MS, Lee SA (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between imaging and pathological findings. Eur Radiol 20:1111–1117
Dogan BE, Gonzalez-Angulo AM, Gilcrease M, Dryden MJ, Yang WT (2010) Multimodality imaging of triple receptor-negative tumors with mammography, ultrasound, and MRI. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:1160–1166
Yang WT, Dryden M, Broglio K et al (2008) Mammographic features of triple receptor-negative primary breast cancers in young premenopausal women. Breast Cancer Res Treat 111:405–410
Whitman GJ, Albarracin CT, Gonzalez-Angulo AM (2011) Triple-negative breast cancer: what the radiologist needs to know. Semin Roentgenol 46:26–39
Chen JH, Agrawal G, Feig B et al (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: MRI features in 29 patients. Ann Oncol 18:2042–2043
Uematsu T, Kasami M, Yuen S (2009) Triple-negative breast cancer: correlation between MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology 250:638–647
Podo F, Buydens LM, Degani H et al (2010) Triple-negative breast cancer: present challenges and new perspectives. Mol Oncol 4:209–229
Woodhams R, Kakita S, Hata H et al (2010) Identification of residual breast carcinoma following neoadjuvant chemotherapy: diffusion-weighted imaging – comparison with contrast-enhanced MR imaging and pathologic findings. Radiology 254:357–366
Allred DC, Harvey JM, Berardo M, Clark GM (1998) Prognostic and predictive factors in breast cancer by immunohistochemical analysis. Mod Pathol 11:155–168
Moeder CB, Giltnane JM, Harigopal M et al (2007) Quantitative justification of the change from 10 % to 30 % for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 scoring in the American Society of Clinical Oncology/College of American Pathologists guidelines: tumor heterogeneity in breast cancer and its implications for tissue microarray based assessment of outcome. J Clin Oncol 25:5418–5425
American College of Radiology (2003) Breast imaging reporting and data system-magnetic resonance imaging. In: American College of Radiology (ed) Breast imaging reporting and data system, 4th edn. American College of Radiology, Reston, pp 1–114
Kuhl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S et al (1999) Dynamic breast MR imaging: are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211:101–110
Koh DM, Collins DJ, Orton MR (2011) Intravoxel incoherent motion in body diffusion-weighted MRI: reality and challenges. AJR Am J Roentgenol 196:1351–1361
Carey LA, Perou CM, Livasy CA et al (2006) Race, breast cancer subtypes, and survival in the Carolina breast cancer study. JAMA 295:2492–2502
Dent R, Trudeau M, Pritchard KI et al (2007) Triple-negative breast cancer: clinical features and patterns of recurrence. Clin Cancer Res 13:4429–4434
Anders C, Carey LA (2008) Understanding and treating triple-negative breast cancer. Oncology (Williston Park) 22:1233–1239
Arnedos M, Nerurkar A, Osin P, A'Hern R, Smith IE, Dowsett M (2009) Discordance between core needle biopsy (CNB) and excisional biopsy (EB) for estrogen receptor (ER), progesterone receptor (PgR) and HER2 status in early breast cancer (EBC). Ann Oncol 20:1948–1952
Lorgis V, Algros MP, Villanueva C et al (2011) Discordance in early breast cancer for tumour grade, estrogen receptor, progesterone receptors and human epidermal receptor-2 status between core needle biopsy and surgical excisional primary tumour. Breast 20:284–287
Tamaki K, Sasano H, Ishida T et al (2010) Comparison of core needle biopsy (CNB) and surgical specimens for accurate preoperative evaluation of ER, PgR and HER2 status of breast cancer patients. Cancer Sci 101:2074–2079
Pal SK, Childs BH, Pegram M (2011) Triple negative breast cancer: unmet medical needs. Breast Cancer Res Treat 125:627–636
Pereira FP, Martins G, de Oliveira C, Rde V (2011) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging of the breast. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 19:95–110
Hamstra DA, Rehemtulla A, Ross BD (2007) Diffusion magnetic resonance imaging: a biomarker for treatment response in oncology. J Clin Oncol 25:4104–4109
Tsushima Y, Takahashi-Taketomi A, Endo K (2009) Magnetic resonance (MR) differential diagnosis of breast tumors using apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) on 1.5-T. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:249–255
Kim SH, Cha ES, Kim HS et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging of breast cancer: correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value with prognostic factors. J Magn Reson Imaging 30:615–620
Guo Y, Cai YQ, Cai ZL et al (2002) Differentiation of clinically benign and malignant breast lesions using diffusion-weighted imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 16:172–178
Razek AA, Gaballa G, Denewer A, Nada N (2010) Invasive ductal carcinoma: correlation of apparent diffusion coefficient value with pathological prognostic factors. NMR Biomed 23:619–623
Costantini M, Belli P, Rinaldi P et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted imaging in breast cancer: relationship between apparent diffusion coefficient and tumour aggressiveness. Clin Radiol 65:1005–1012
Padhani AR, Liu G, Koh DM et al (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging as a cancer biomarker: consensus and recommendations. Neoplasia 11:102–125
Park SH, Moon WK, Cho N et al (2010) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging: pretreatment prediction of response to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in patients with breast cancer. Radiology 257:56–63
Jeh SK, Kim SH, Kim HS et al (2011) Correlation of the apparent diffusion coefficient value and dynamic magnetic resonance imaging findings with prognostic factors in invasive ductal carcinoma. J Magn Reson Imaging 33:102–109
Matsuoka A, Minato M, Harada M et al (2008) Comparison of 3.0- and 1.5-Tesla diffusion-weighted imaging in the visibility of breast cancer. Radiat Med 26:15–20
Acknowledgement
This study was supported by a faculty research grant of Yonsei University College of Medicine for 2011 (6-2011-0191).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Youk, J.H., Son, E.J., Chung, J. et al. Triple-negative invasive breast cancer on dynamic contrast-enhanced and diffusion-weighted MR imaging: comparison with other breast cancer subtypes. Eur Radiol 22, 1724–1734 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2425-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-012-2425-2