Abstract
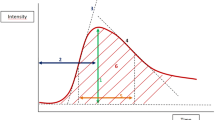
The purpose of this exploratory study was to correlate kinetic and morphologic MR features with histologic prognostic factors in invasive breast cancer. Sixty-one women with invasive breast cancer underwent dynamic contrast-enhanced MR imaging at 1.5 T, using T1-weighted 3D fast low-angle shot technique. The MR characteristics were correlated with classical pathologic prognostic factors (tumor size, histologic type, grade and lymph node status) and immunohistochemically detected biomarkers [c-erbB-2, p53, Ki-67, and estrogen receptor (ER)]. Univariate and multivariate statistical analyses were performed. Presence of rim enhancement pattern, early maximal enhancement and washout phenomenon were independently associated with established predictors of poor prognosis (higher histologic grade, positive Ki-67, and negative ER status). Our results suggest that these MR signs are not only important in differentiating benign from malignant lesions, but may also be useful to noninvasively identify highly aggressive breast carcinomas.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Orel SG, Schnall MD (2001) MR imaging of the breast for the detection, diagnosis, and staging of breast cancer. Radiology 220:13–30
Hrung JM, Sonnad SS, Schwartz JS, Langlotz CP (1999) Accuracy of MR imaging in the work-up of suspicious breast lesions: a diagnostic meta-analysis. Acad Radiol 6:387–397
Boetes C, Barentsz JO, Mus RD et al. (1994) MR characterization of suspicious breast lesions with a gadolinium-enhanced TurboFLASH subtraction technique. Radiology 193:777–781
Orel SG, Schnall MD, LiVolsi VA, Troupin RH (1994) Suspicious breast lesions: MR imaging with radiologic–pathologic correlation. Radiology 190:485–493
Kuhl CK, Mielcareck P, Klaschik S et al. (1999) Dynamic breast MR imaging: are signal intensity time course data useful for differential diagnosis of enhancing lesions? Radiology 211:101–110
Abraham DC, Jones RC, Jones SE et al. (1996) Evaluation of neoadjuvant chemotherapeutic response of locally advanced breast cancer by magnetic resonance imaging. Cancer 78:91–100
Boné B, Aspelin P, Bronge L, Veress B (1998) Contrast-enhanced MR imaging as a prognostic indicator of breast cancer. Acta Radiol 39:279–284
Mussurakis S, Buckley DL, Horsman A (1997) Dynamic MR imaging of invasive breast cancer: correlation with tumour grade and other histological factors. Br J Radiol 70:446–451
Stomper PC, Herman S, Klippenstein DL et al. (1995) Suspect breast lesions: findings at dynamic gadolinium-enhanced MR imaging correlated with mammographic and pathologic features. Radiology 197:387–395
Fischer U, Kopka L, Brinck U, Korabiowska M, Schauer A, Grabbe E (1997) Prognostic value of contrast-enhanced MR mammography in patients with breast cancer. Eur Radiol 7:1002–1005
Elston CW, Ellis IO, Pinder SE (1999) Pathological prognostic factors in breast cancer. Crit Rev Oncol Hematol 31:209–223
Yaghan R, Stanton PD, Robertson KW, Going JJ, Murray GD, McArdle CS (1998) Oestrogen receptor status predicts local recurrence following breast conservation surgery for early breast cancer. Eur J Surg Oncol 24:424–426
Lovekin C, Ellis IO, Locker A et al. (1991) c-erbB-2 oncoprotein expression in primary and advanced breast cancer. Br J Cancer 63:439–443
Bergh J (1999) Clinical studies of p53 in treatment and benefit of breast cancer patients. Endocr Relat Cancer 6:51–59
Scholzen T, Gerdes J (2000) The Ki-67 protein: from the known and the unknown. J Cell Physiol 182:311–322
Fox SB (1997) Tumour angiogenesis and prognosis. Histopathology 30:294–301
Weidner N, Semple JP, Welch WR, Folkman J (1991) Tumor angiogenesis and metastasis: correlation in invasive breast carcinoma. N Engl J Med 324:1–8
Gasparini G, Harris AL (1995) Clinical importance of determination of tumor angiogenesis in breast carcinoma: much more than a new prognostic tool. J Clin Oncol 13:765–782
Heimann R, Ferguson D, Powers C, Recant WM, Weichselbaum RR, Hellman S (1996) Angiogenesis as a predictor of long-term survival for patients with node-negative breast cancer. J Natl Cancer Inst 88:1764–1769
Axelsson K, Ljung BM, Moore DH II et al. (1995) Tumor angiogenesis as a prognostic assay for invasive ductal breast carcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst 87:997–1008
Goulding H, Abdul-Rashid NF, Robertson JF et al. (1995) Assessment of angiogenesis in breast carcinoma: an important factor in prognosis? Hum Pathol 26:1196–1200
Frouge C, Guinebretiere JM, Contesso G, Paola R di, Blery M (1994) Correlation between contrast-enhancement in dynamic magnetic resonance imaging of the breast and tumor angiogenesis. Invest Radiol 29:1043–1049
Buadu LD, Murakami J, Murayama S et al. (1996) Breast lesions: correlation of contrast medium enhancement patterns on MR images with histopathologic findings and tumor angiogenesis. Radiology 200:639–649
Buckley DL, Drew PJ, Mussurakis S, Monson JR, Horsman A (1997) Microvessel density of invasive breast cancer assessed by dynamic Gd-DTPA enhanced MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging 7:461–464
Nunes LW, Schnall MD, Orel SG et al. (1997) Breast MR imaging: interpretation model. Radiology 202:833–841
Schnall MD, Rosten S, Englander S, Orel SG, Nunes LW (2001) A combined architectural and kinetic interpretation model for breast MR images. Acad Radiol 8:591–597
Kaiser WA, Zeitler E (1989) MR imaging of the breast: fast imaging sequences with and without Gd-DTPA. Preliminary observations. Radiology 170:681–686
Heywang SH, Wolf A, Pruss E, Hilbertz T, Eiermann W, Permanetter W (1989) MR imaging of the breast with Gd-DTPA: use and limitations. Radiology 171:95–103
Stack JP, Redmond OM, Codd MB, Dervan PA, Ennis JT (1990) Breast disease: tissue characterization with Gd-DTPA enhancement profiles. Radiology 174:491–494
Heywang-Köbrunner SH, Bick U, Bradley WG Jr et al. (2001) International investigation of breast MRI: results of a multicentre study (11 sites) concerning diagnostic parameters for contrast-enhanced MRI based on 519 histopathologically correlated lesions. Eur Radiol 11:531–546
Ikeda O, Yamashita Y, Morishita S et al. (1999) Characterization of breast masses by dynamic-enhanced MR imaging: a logistic regression analysis. Acta Radiol 40:585–592
Elston CW (1987) Grading of invasive carcinoma of the breast. In: Page DL, Anderson TJ (eds) Diagnostic histopathology of the breast, 1st edn. Churchill Livingstone, Edinburgh, pp 300–311
Jatoi I, Hilsenbeck SG, Clark GM, Osborne CK (1999) Significance of axillary lymph node metastasis in primary breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 17:2334–2340
Mirza AN, Mirza NQ, Vlastos G, Singletary SE (2002) Prognostic factors in node-negative breast cancer: a review of studies with sample size more than 200 and follow-up more than 5 years. Ann Surg 235:10–26
Weidner N (1995) Current pathologic methods for measuring intratumoral microvessel density within breast carcinoma and other solid tumors. Breast Cancer Res Treat 36:169–180
Jong J, van Diest P, Baak JP (1995) Heterogeneity and reproducibility of microvessel counts in breast cancer. Lab Invest 73:922–926
Ahlgren J, Risberg B, Villman K, Bergh J (2002) Angiogenesis in invasive breast carcinoma: a prospective study of tumour heterogeneity. Eur J Cancer 38:64–69
Gasparini G (2000) Prognostic value of vascular endothelial growth factor in breast cancer. Oncologist 5 (Suppl 1):37–44
Hulka CA, Edmister WB, Smith BL et al. (1997) Dynamic echo-planar imaging of the breast: experience in diagnosing breast carcinoma and correlation with tumor angiogenesis. Radiology 205:837–842
Helbich TH, Roberts TP, Gossmann A et al. (2000) Quantitative gadopentetate-enhanced MRI of breast tumors: testing of different analytic methods. Magn Reson Med 44:915–924
Knopp MV, Weiss E, Sinn HP et al. (1999) Pathophysiologic basis of contrast enhancement in breast tumors. J Magn Reson Imaging 10:260–266
Wedegartner U, Bick U, Wortler K, Rummeny E, Bongartz G (2001) Differentiation between benign and malignant findings on MR mammography: usefulness of morphological criteria. Eur Radiol 11:1645–1650
Mussurakis S, Buckley DL, Drew PJ et al. (1997) Dynamic MR imaging of the breast combined with analysis of contrast agent kinetics in the differentiation of primary breast tumours. Clin Radiol 52:516–526
Schnall MD (2001) An overview of interpretation strategies for breast MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 9:289–294
Matsubayashi R, Matsuo Y, Edakuni G, Satoh T, Tokunaga O, Kudo S (2000) Breast masses with peripheral rim enhancement on dynamic contrast-enhanced MR images: correlation of MR findings with histologic features and expression of growth factors. Radiology 217:841–848
Stomper PC, Herman S, Klippenstein DL, Winston JS, Budnick RM, Stewart CC (1996) Invasive breast carcinoma: analysis of dynamic magnetic resonance imaging enhancement features and cell proliferative activity determined by DNA S-phase percentage. Cancer 77:1844–1849
Sherif H, Mahfouz AE, Oellinger H et al. (1997) Peripheral washout sign on contrast-enhanced MR images of the breast. Radiology 205:209–213
Linderholm B, Tavelin B, Grankvist K, Henriksson R (1998) Vascular endothelial growth factor is of high prognostic value in node-negative breast carcinoma. J Clin Oncol 16:3121–3128
Kumar R, Yarmand-Bagheri R (2001) The role of HER2 in angiogenesis. Semin Oncol 28(Suppl 16):27–32
Izumi Y, Xu L, Tomaso E di, Fukumura D, Jain RK (2002) Tumour biology: herceptin acts as an anti-angiogenic cocktail. Nature 416:279–280
Nakopoulou L, Stefanaki K, Panayotopoulou E et al. (2002) Expression of the vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-2/Flk-1 in breast carcinomas: correlation with proliferation. Hum Pathol 33:863–870
Bone B, Wiberg MK, Parrado C, Falkmer U, Aspelin P, Gad A (1998) Mechanism of contrast enhancement in breast lesions at MR imaging. Acta Radiol 39:494–500
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Szabó, B.K., Aspelin, P., Kristoffersen Wiberg, M. et al. Invasive breast cancer: correlation of dynamic MR features with prognostic factors. Eur Radiol 13, 2425–2435 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2000-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-003-2000-y