Abstract
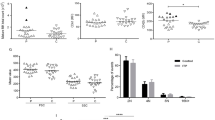
Platelet and leukocyte activation has been demonstrated in polycythemia vera (PV) and essential thrombocythemia (ET), but such information is limited in primary myelofibrosis (PMF). Platelet, leukocyte, endothelial, and coagulation activation status was assessed in 26 PMF patients and compared with data from 22 age- and sex-matched healthy individuals. Study included flow cytometry assessment of platelet P-selectin expression [at baseline and after adenosine diphosphate (ADP), thrombin and arachidonic acid stimulation], platelet–neutrophil and platelet–monocyte complexes, and CD11b expression in neutrophils and monocytes. Additionally, soluble P-selectin, sCD40L, tissue factor, thrombomodulin, prothrombin fragment 1 + 2 (F1 + 2), and D-dimer were measured by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assays. The above parameters were correlated with the patients’ clinical data and presence of the JAK2 V617F mutation. Compared with controls, PMF patients had increased baseline platelet activation, as shown by significantly higher levels of soluble and platelet P-selectin expression, and also higher percentages of platelet–monocyte complexes. Neutrophil and monocyte CD11b expression was significantly higher in patients with the JAK2 mutation than in those with wild-type allele or the controls. Endothelial and coagulation activation, as demonstrated by increased plasma levels of thrombomodulin and F1 + 2, was also found in PMF, with patients with the JAK2 mutation showing significantly higher values of F1 + 2 than those with wild-type allele. In conclusion, PMF patients have platelet, leukocyte, endothelial, and coagulation activation similar to that in PV and ET. CD11b overexpression and F1 + 2 are correlated with the presence of the JAK2 mutation.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alvarez-Larrán A, Garcia-Pagan JC, Abraldes JG, Arellano E, Reverter JC, Bosch J, Cervantes F (2004) Increased CD11b neutrophil expression in Budd-Chiari syndrome or portal vein thrombosis secondary to polycythemia vera. Br J Haematol 124:329–335
André P, Hartwell D, Hrachovinová I, Saffaripour S, Wagner DD (2000) Pro-coagulant state resulting from high levels of soluble P-selectin in blood. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 97:13835–13840
Arellano-Rodrigo E, Alvarez-Larrán A, Reverter JC, Villamor N, Colomer D, Cervantes F (2006) Increased platelet and leukocyte activation as contributing mechanisms for thrombosis in essential thrombocythemia and correlation with the JAK2 mutational status. Haematologica 91:169–175
Barosi G, Ambrosetti A, Finelli G, Grossi A, Leoni P, Liberato NL, Petti MC, Pogliani E, Ricetti M, Rupoli S, Visani G, Tura S (1999) The Italian Consensus Conference on Diagnostic Criteria for Myelofibrosis with Myeloid Metaplasia. Br J Haematol 104:730–737
Baxter EJ, Scott LM, Campbell PJ, East C, Fourouclas N, Swanton S, Vassiliou GS, Bench AJ, Boyd EM, Curtin N, Scott MA, Erber WN, Green A (2005) Acquired mutation of the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in human myeloproliferative disorders. Lancet 365:1054–1061
Besses C, Cervantes F, Pereira A, Florensa L, Sole F, Hernandez-Boluda JC, Woessner S, Sans-Sabrafen J, Rozman C, Montserrat E (1999) Major vascular complications in essential thrombocythemia: a study of the predictive factors in a series of 148 patients. Leukemia 13:50–154
Boehme MWJ, Galle P, Stremmel W (2002) Kinetics of thrombomodulin release and endothelial cell injury by neutrophil-derived proteases and oxygen radicals. Immunology 107:340–349
Cervantes F, Pereira A, Esteve J, Rafel M, Cobo F, Rozman C, Montserrat E (1997) Identification of ‘short-lived’ and ‘long-lived’ patients at presentation of idiopathic myelofibrosis. Br J Haematol 97:635–640
Cervantes F, Alvarez-Larrán A, Arellano-Rodrigo E, Granell M, Domingo A, Montserrat E (2006) Frequency and risk factors for thrombosis in idiopathic myelofibrosis: analysis in a series of 155 patients from a single institution. Leukemia 20:55–60
Conway EM, Nowakowski B, Steiner-Mosonyi M (1992) Human neutrophils synthesize thrombomodulin that does not promote thrombin-dependent protein C activation. Blood 80:1254–1263
Elliott MA, Tefferi A (2005) Thrombosis and haemorrhage in polycythaemia vera and essential thrombocythaemia. Br J Haematol 128:275–290
Engstad CS, Lia K, Rekdal O, Olsen JO, Osterud B (1995) A novel biological effect of platelet factor 4 (PF4): enhancement of LPS-induced tissue factor activity in monocytes. J Leuk Biol 58:575–581
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Evangelista V, Vignoli A, Licini M, Balicco M, Manarini S, Finazzi G, Cerletti C, Barbui T (2000) Polymorphonuclear leukocyte activation and hemostasis in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Blood 96:4261–4266
Falanga A, Marchetti M, Vignoli A, Balducci D, Barbui T (2005) Leukocyte-platelet interaction in patients with essential thrombocythemia and polycythemia vera. Exp Hematol 33:523–530
Fijnheer R, Frijns CJM, Korteweg J, Rommes H, Peters JH, Sixma JJ, Nieuwenhuis HK (1997) The origin of P-selectin as a circulating plasma protein. Thromb Haemost 77:181–185
Gruppo Italiano Studio Policitemia (1995) Polycythemia vera: the natural history of 1213 patients followed for 20 years. Ann Intern Med 123:656–664
James C, Ugo V, Le Couédic JP, Staerk J, Delhommeau F, Lacout C, Garcon L, Raslova H, Berger R, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Villeval JL, Constantinescu SN, Casadevall N, Vainchenker W (2005) A unique clonal JAK2 mutation leading to constitutive signaling causes polycythemia vera. Nature 434:1144–1148
Jensen MK, de Nully Brown P, Lund BV, Nielsen OJ, Hasselbalch HC (2000) Increased platelet activation and abnormal glycoprotein content and redistribution in myeloproliferative disorders. Br J Haematol 110:116–124
Jensen MK, de Nully Brown P, Lund BV, Nielsen OJ, Hasselbalch HC (2001) Increased circulating platelet-leukocytes aggregates in myeloproliferative disorders is correlated to previous thrombosis, platelet activation and platelet count. Eur J Haematol 66:143–151
Jensen MK, Riisbro R, de Nully Brown P, Brunner N, Hasselbach HC (2002) Elevated soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor in plasma from patients with idiopathic myelofibrosis or polycythemia vera. Eur J Haematol 69:43–49
Kralovics R, Passamonti F, Buser AS, Teo SS, Tiedt R, Passweg JR, Tichelli A, Cazzola M, Skoda RC (2005) A gain-of-function mutation of JAK2 in myeloproliferative disorders. New Engl J Med 352:1779–1790
Lennert K, Naghai K, Schwarze EW (1975) Patho-anatomical features of the bone marrow. Clin Haematol 43:331–351
Leoni P, Rupoli S, Lai G, Brunelli MA, Belmonte MM, Pugnaloni A, Rabini RA, Mazzanti L, Biagini G (1994) Platelet abnormalities in idiopathic myelofibrosis: functional, biochemical and immunomorphological correlations. Haematologica 79:29–39
Levine RL, Wadleigh M, Cools J, Ebertm BL, Wernig G, Huntly BJ, Boggon TJ, Wlodarska I, Clark JJ, Moore S, Adelsperger J, Koo S, Lee JC, Gabriel S, Mercher T, D’Andrea A, Frohling S, Dohner K, Marynen P, Vandenberghe P, Mesa RA, Tefferi A, Griffin JD, Eck MJ, Sellers WR, Meyerson M, Golub TR, Lee SJ, Gilliland DG (2005) Activating mutation in the tyrosine kinase JAK2 in polycythemia vera, essential thrombocythemia and myeloid metaplasia with myelofibrosis. Cancer Cell 7:387–397
Schmitt A, Jouault H, Guichard J, Wendling F, Drouin A, Cramer EM (2000) Pathologic interaction between megakaryocytes and polymorphonuclear leukocytes in myelofibrosis. Blood 96:1342–1347
Schmitz G, Rothe G, Ruf A, Barlage S, Tschope D, Clemetson KJ, Goodall AH, Michelson AD, Nurden AT, Shankey TV (1998) European Working Group on clinical cell analysis: consensus protocol for the flow cytometric characterisation of platelet function. Thromb Haemost 79:885–896
Shattil SJ, Cunningham M, Hoxie JA (1987) Detection of activated platelets in whole blood using activation-dependent monoclonal antibodies and flow cytometry. Blood 70:307–315
Tefferi A, Lasho TL, Steensma DP, Mesa RA, Li CY, Wadleigh M, Gilliland DG (2005) The JAK2V617F tyrosine kinase mutation in myelofibrosis with myeloid metaplasia: lineage specificity and clinical correlates. Br J Haematol 131:320–328
Viallard JF, Solanilla A, Gauthier B, Contin C, Déchanet J, Grosset C, Moreau JF, Praloran V, Nurden P, Pellegrin JL, Nurden AT, Ripoche J (2002) Increased soluble and platelet-associated CD40 ligand in essential thrombocythemia and reactive thrombocytosis. Blood 99:2612–2614
Villmow T, Kemkes-Matthes B, Matzdorff AC (2003) Markers of platelet activation and platelet-leukocyte interaction in patients with myeloproliferative syndromes. Thromb Res 108:139–145
Acknowledgements
We thank the personnel of the Laboratories of Hemostasis and Hemopathology of the Hospital Clínic for their excellent technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Alvarez-Larrán, A., Arellano-Rodrigo, E., Reverter, J.C. et al. Increased platelet, leukocyte, and coagulation activation in primary myelofibrosis. Ann Hematol 87, 269–276 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0386-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00277-007-0386-3