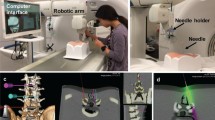
Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate a commercially available robotic assistance device for computed tomography-guided diagnostic and therapeutic interventions, compared to regular, manually performed CT scan-guided interventions in terms of precision, exposure to radiation to the patient and intervention time.
Materials and Methods
Over a period of 6 months, 55 consecutive patients were recruited and treated using robotic assistance and compared to a control group of 101 patients previously treated with a regular CT scan-guided, manual approach. Evaluated parameters were precision (deviation from planned target and number of needle replacements), radiation exposure to the patient and intervention time. Evaluations were performed with regard to complexity (in-plane vs out-of-plane interventions) and type of anesthesia (general vs local).
Results
Parameters related to precision were in general significantly better in the robotic assistance group (p < 0.01) with a mean deviation of 1.2 mm (± 1.6 mm) compared to 2.6 mm (± 1.1 mm) in the comparison group. Compared to manual procedure, the mean intervention time was reduced by 15 min (± 5.4 min) on average for an out-of-plane needle placement in the robotic group. There was no increase of exposure to radiation to the patient while radiation exposure for the physician was reduced to zero when the navigation system was used.
Conclusion
Compared to manual placement, the use of a robotic assistance device in out-of-plane CT-guided interventions under general anesthesia allows for probe placement with high precision. Intervention time is reduced with no increase of exposure to radiation to the patient.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sarti M, Brehmer WP, Gay SB. Low-dose techniques in CT-guided interventions. Radiographics. 2012; 32(4): 1109–19; discussion 1119–20.
van Vledder MG, et al. Development of hepatic pseudotumors for image-guided interventional and surgical research in a large animal model. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2011;22(10):1452–6.
Mbalisike EC, et al. Image-guided microwave thermoablation of hepatic tumours using novel robotic guidance: an early experience. Eur Radiol. 2015;25(2):454–62.
Schulz B, et al. Computed tomography guided percutaneous liver biopsy using a robotic assistance device—a corpse study. Open J Radiol. 2015;5:84–91.
Bale R, Widmann G. Navigated CT-guided interventions. Minim Invasive Ther Allied Technol. 2007;16(4):196–204.
Rouchy RC, et al. Evaluation of the clinical benefit of an electromagnetic navigation system for CT-guided interventional radiology procedures in the thoraco-abdominal region compared with conventional CT guidance (CTNAV II): study protocol for a randomised controlled trial. Trials. 2017;18(1):306.
Klingler JH, et al. First experience using navigation-guided radiofrequency kyphoplasty for sacroplasty in sacral insufficiency fractures. Rofo. 2013;185(8):733–40.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state no conflict of interest for any aspect of the submitted work.
Ethical Approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Smakic, A., Rathmann, N., Kostrzewa, M. et al. Performance of a Robotic Assistance Device in Computed Tomography-Guided Percutaneous Diagnostic and Therapeutic Procedures. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 41, 639–644 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1841-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1841-8