Abstract
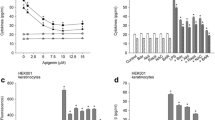
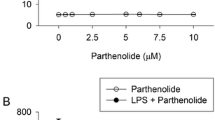
Objective and Design: Topical application of anthralin, used in the treatment of psoriasis, is often accompanied by severe skin inflammation, presumably due to free radical products of the drug. The role of inflammatory cytokines and their induction by anthralin-derived reactive oxygen species were studied in cultures of normal human keratinocytes (NHKs).¶Materials and Methods: Anthralin was added to cultures of NHKs in the presence or absence of various antioxidants, including superoxide dismutase, tetramethylthiourea, N-acetylcysteine and vitamin E and relative changes in cytokine secretion and in the number of mRNA transcripts were examined. In addition, NHKs were either treated with neutralizing antibodies to tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α or transfected with a CAT-linked IL-8 promoter to establish the direct effects of anthralin on chemokine synthesis.¶Results: Anthralin, at concentrations between 5 μM and 25μM, caused a marked increase in granulocyte macrophage-colony stimulating factor (GM-CSF), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8 and TNFα synthesis that was selectively inhibited by specific antioxidants. Furthermore, anthralin induced chemokine secretion without the need of primary cytokines.¶Conclusions: Taken together, these studies suggest that oxygen radicals generated from anthralin are responsible for the induction of inflammatory cytokines which, in turn contributes to their dermal toxicity.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received 27 June 1997; returned for revision 20 August 1997; accepted by G. W. Carter 18 December 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lange, R., Hayden, P., Chignell, C. et al. Anthralin stimulates keratinocyte-derived proinflammatory cytokines via generation of reactive oxygen species. Inflamm. res. 47, 174–181 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050313
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s000110050313