Summary
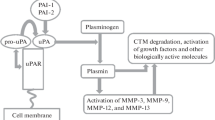
The plasminogen activation system consists of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors, serine proteases, and serpins. The proteases and inhibitors regulate a variety of processes in tissue morphogenesis, differentiation, cell migration, and cancer cell invasiveness and metastasis. One of the plasminogen activators, urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA), binds to a specific surface and provides a localized cell surface proteolytic activity required for the destruction of extracellular matrix, which is a vital step in tumor cell invasion. The proteolytic activity of uPA is modulated by its cell surface receptor, as well as by plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 (PAI-1) and, to a lesser degree, by other inhibitors.
The role of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in cancer invasion can be demonstrated in the development and progression of malignant brain tumors. Our findings indicate that uPA and PAI-1 expression are dramatically upregulated in malignant brain tumors in parallel with the histological progression of the tumors. The results suggest that these molecules may contribute to tumor invasion in addition to their significant role in angiogenesis. An evaluation of the plasminogen activation system could add diagnostic and prognostic significance to the evaluation of individual patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Liotta LA, Steeg PS, Stetler-Stevenson WG: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive and negative regulation. Cell 64: 327–336, 1991
Vassalli JD, Sappino AP, Belin D: The plasminogen activator/plasmin system. J Clin Invest 88: 1067–1072, 1991
Blasi F, Vassalli J-D, Danø K: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator: proenzyme, receptor, and inhibitors. J Cell Biol 104: 801–804, 1987
Danø K, Andreasen PA, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Kristensen P, Nielsen LS, Skriver L: Plasminogen activators, tissue degradation, and cancer. Adv Cancer Res 44: 139–266, 1985
Pöllänen J, Stephens RW, Vaheri A: Directed plasminogen activation at the surface of normal and malignant cells. Adv Cancer Res 57: 273–328, 1991
Saksela O: Plasminogen activation and regulation of pericellular proteolysis. Biochim Biophys Acta 823: 35–65, 1985
Pennica D, Holmes WE, Kohr WJ, Harkins RN, Vehar GA, Ward CA, Bennett WF, Yelverton E, Seeburg PH, Heyneker HL, Goeddel DV: Cloning and expression of human tissue-type plasminogen activator cDNA inE. Coli. Nature 301: 214–221, 1983
Riccio A, Grimaldi G, Verde P, Sebastio G, Boast S, Blasi F: The human urokinase-plasminogen activator gene and its promoter. Nucleric Acids Res 13: 2759–2771, 1985
Laiho M, Keski-Oja J: Growth factors in the regulation of pericelluar proteolysis. A review. Cancer Res 49: 2533–2553, 1989
Wolf BB, Vasudevan J, Henkin J, Gonias SL: Nerve growth factor-γ activites soluble and receptor-bound single chain urokinase-type plasminogen activator. J Biol Chem 268: 16327–16331, 1993
He C, Wilhelm SM, Pentland AP, Marmer BL, Grant GA, Eisen AZ, Goldberg GI: Tissue cooperation in a proteolytic cascade activating human interstitial collagenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 2632–2636, 1989
Reich P, Thompson EW, Iwamoto Y, Martin GR, Deason JR, Fuller GC, Miskin R: Effects of inhibitors of plasminogen activator, serine proteases, and collagenase IV on the invasion of basement membranes by metastatic cells. Cancer Res 48: 3307–3312, 1988
Hart DA, Rehemtulla A: Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors: regulators of extracellular proteolysis and cell function. Comp Biochem Physiol (B) 90: 691–708, 1988
Andreasen PA, Nielsen LS, Kristensen P, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Skriver L, Danø K: Plasminogen activator inhibitor from human fibrosarcoma cells binds urokinase-type plasminogen activator, but not its proenzyme. J Biol Chem 261: 7644–7651, 1986
Coleman PL, Patel PD, Cwikel BJ, Rafferty UM, Sznycer-Laszuk R, Gelehrter TD: Characterization of the dexamethasone-induced inhibitor of plasminogen activator in HTC hepatoma cells. J Biol Chem 261: 4352–4357, 1986
Ellis V, Danø K: Plasminogen activator by receptor-bound urokinase. Semin Thromb Hemost 17: 194–200, 1991
Erickson LA, Hekman CM, Loskutoff DJ: The primary plasminogen activator inhibitors in endothelial cells, platelets, serum, and plasma are immunologically related. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 8710–8714, 1985
Heidtmann H-H, Hofmann M, Jacob E, Erbil C, Havemann K, Schwartz-Albiez R: Synthesis and secretion of plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors in cell lines of different groups of human lung tumors. Cancer Res 49: 6960–6965, 1989
Kooistra T, Sprengers ED, Van Hinsbergh VW: Rapid inactivation of the plasminogen-activator inhibitor upon secretion from cultured human endothelial cells. Biochem J 239: 497–504, 1986
Levin EG, Santell L: Conversion of the active to latent plasminogen activator inhibitor from human endothelial cells. Blood 70: 1090–1098, 1987
Mimuro J, Schleef RR, Loskutoff DJ: Extracellular matrix of cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells contains functionally active type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Blood 70: 721–728, 1987
Reilly CF, McFall RC: Platelet-derived growth factor and transforming growth factor-β regulate plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 synthesis in vascular smooth muscle cells. J Biol Chem 266: 9419–9427, 1991
Cajot JF, Bamat J, Bergonzelli GE, Kruithof EKO, Medcalf RL, Testuz J, Sordat B: Plasminogen-activator inhibitor type 1 is a potent natural inhibitor of extracellular matrix degradation by fibrosarcoma and colon carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 87: 6939–6943, 1990
Hagège J, Peraldi MN, Rondeau E, Adida C, Delarue F, Medcalf R, Schleuning WD, Sraer JD: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 deposition in the extracellular matrix of cultured human mesangial cells. Am J Pathol 141: 117–128, 1992
Pöllänen J, Hedman K, Nielsen LS, Danø K, Vaheri A: Ultrastructural localization of plasma membrane-associated urokinase-type plasminogen activator at focal contacts. J Cell Biol 106: 87–95, 1988
Schleef RR, Podor TJ, Dunne E, Mimuro J, Loskutoff DJ: The majority of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor associated with cultured human endothelial cells is located under the cells and is accessible to solution-phase tissue-type plasminogen activator. J Cell Biol 110: 155–163, 1990
Cubellis MV, Andreasen P, Ragno P, Mayer M, Danø K, Blasi F: Accessibility of receptor-bound urokinase to type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 4828–4832, 1989
Ellis V, Wun TC, Behrendt N, Rønne E, Danø K: Inhibition of receptor-bound urokinase by plasminogen-activator inhibitors. J Biol Chem 265: 9904–9908, 1990
Kundsen BS, Harpel PC, Nachman RL: Plasminogen activator inhibitor is associated with the extracellular matrix of cultured bovine smooth muscle cells. J Clin Invest 80: 1082–1089, 1987
Ossowski L, Russo-Payne H, Wilson EL: Inhibition of urokinase-type plasminogen activator by antibodies: The effect on dissemination of a human tumor in the nude mouse. Cancer Res 51: 274–281, 1991
Crowley CW, Cohen RL, Lucas BK, Liu G, Shuman MA, Levinson AD: Prevention of metastasis by inhibition of the urokinase receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90: 5021–5025, 1993
Mohanam S, Sawaya R, McCutcheon I, Ali-Osman F, Boyd D, Rao JS: Modulation ofin vitro invasion of human glioblastoma cells by urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor antibody. Cancer Res 53: 4143–4147, 1993
Laug WE, Cao XR, Yu YB, Shimada H, Kruithof EKO: Inhibition of invasion of HT1080 sarcoma cells expressing recombinant plasminogen activator inhibitor 2. Cancer Res 53: 6051–6057, 1993
Montgomery AMP, De Clerck YA, Langley KE, Reisfeld RA, Mueller BM: Melanoma-mediated dissolution of extracellular matrix: contribution of urokinase-dependent and metalloproteinase-dependent proteolytic pathways. Cancer Res 53: 693–700, 1993
Bergman BL, Scott RW, Bajpai A, Watt S, Baker JB: Inhibition of tumor-cell-mediated extracellular matrix destruction by a fibroblast protease inhibitor, protease nexin I. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83: 996–1000, 1986
Blasi F: Urokinase and urokinase receptor: a paracrine/autocrine system regulating cell migration and invasiveness. Bioessays 15: 105–111, 1993
Russel DC, Rubinstein LJ: Pathology of tumors of the nervous system. Edward Arnold, (5 ed) London, 1989
Burger PC, Dubois PJ, Schold SCJr, Smith KRJr, Odom GL, Crafts DC, Giangaspero F: Computerized tomographic and pathologic studies of the untreated, quiescent, and recurrent glioblastoma maltiforme. J Neurosurg 58: 159–169, 1983
Folkman J, Watson K, Ingber D, Hanahan D: Induction of angiogenesis during the transition from hyperplasia to neoplasia. Nature 339: 58–61, 1989
Goldfarb RH, Ziehe M, Murano G, Liotta LA: Plasminogen activators (Urokinase) mediate neovascularization: possible role in tumor angiogenesis. Semin Thromb Hemost 12: 337–338, 1986
Pepper MS, Vassalli J-D, Montesano R, Orci L: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is induced in migrating capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 105: 2535–2541, 1987
Sawaya R: The fibrinolytic enzymes in the biology of brain tumors. In: Sawaya R (ed) Fibrinolysis and the central nervous system. Hanley & Belfus, Inc., Philadelphia, 1990, pp 106–126
Collen D: On the regulation and control of fibrinolysis. Edward Kowalski Memorial Lecture. Thromb Haemost 43: 77–89, 1980
Moonen G, Grau-Wagemans MP, Selak I, Lefebvre PP, Rogister B, Vassalli JD, Belin D: Plasminogen activator is a mitogen for astrocytes in developing cerebellum. Brain Res 352: 41–48, 1985
Qian Z, Gilbert ME, Colicos MA, Kandel ER, Kuhl D: Tissue-plasminogen activator is induced as an immediate-early gene during seizure, kindling and long-term potentiation. Nature 361: 453–457, 1993
Krystosek A, Seeds NW: Plasminogen activator release at the neuronal growth cone. Science 213: 1532–1534, 1981
Moonen G, Grau-Wagemans MP, Selak I: Plasminogen activator-plasmin system and neuronal migration. Nature 298: 753–755, 1982
Sawaya R, Highsmith R: Plasminogen activator activity and molecular weight patterns in human brain tumors. J Neurosurg 68: 73–79, 1988
Sawaya R, Rämö OJ, Shi ML, Mandybur G: Biological significance of tissue plasminogen activator content in brain tumors. J Neurosurg 74: 480–486, 1991
de Vries TJ, Quax PHA, Denijn M, Verrijp KN, Verheijpen JH, Verspaget HW, Weidle UH, Ruiter DJ, van Muijen GNP: Plasminogen activators, their inhibitors, and urokinase receptor emerge in late stages of melanocytic tumor progression. Am J Pathology 144: 70–81, 1994
Ossowski L, Biegel D, Reich E: Mammary plasminogen activator: correlation with involution, hormonal modulation and comparison between normal and neoplastic tissue. Cell 16: 929–940, 1979
Goldfarb RH, Murano G, Brundage R, Siegal GP, Terranova V, Garbisa S, Liotta LA: Degradation of glycoprotein and collagenous components of the basement membrane: studies with urokinase-type plasminogen activator, α-thrombin, and plasmin. Semin Thromb Hemost, 12: 335–336, 1986
Ichinose A, Fujikawa K, Suyama T: The activation of prourokinase by plasmin kallikrein and its inactivation by thrombin. J Biol Chem 261: 3486–3489, 1986
Kobayashi H, Schmitt M, Goretzki L, Chucholowski N, Calvete J, Kramer M, Günzler WA, Jänicke F, Graeff H: Cathepsin B efficiently activates the soluble and the tumor cell receptor-bound form of the proenzyme urokinase-type plasminogen activator (pro-uPA). J Biol Chem 266: 5147–5152, 1991
Sappino A, Busso N, Belin D, Vassalli JD: Increase of urokinase-type plasminogen activator gene expression in human lung and breast carcinomas. Cancer Res 47: 4043–4046, 1987
Oka T, Ishida T, Nishino T, Sugimachi K: Immunohistochemical evidence of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in primary and metastatic tumors of pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 51: 3522–3525, 1991
Duffy MJ, Reilly D, O'Sullivan C, O'Higgins N, Fennelly JJ, Andreasen P: Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a new and independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer Res 50: 6827–6829, 1990
Foekens JA, Schmitt M, van Putten WLJ, Peters HA, Bontenbal M, Jänicke F, Klijn JGM: Prognostic value of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in 671 primary breast cancer patients. Cancer Res 52: 6101–6105, 1992
Grøndahl-Hansen J, Christensen IJ, Rosenquist C, Brünner N, Møuridsen HT, Danø K, Blichert-Toft M: High levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and its inhibitor PAI-1 in cytosolic extracts of breast carcinomas are associated with poor prognosis. Cancer Res 53: 2513–2521, 1993
Jänicke F, Schmitt M, Ulm K, Gössner W, Graeff H: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen and early relapse in breast cancer. Lancet ii: 1049, 1989
Reilly D, Christensen L, Duch M, Nolan N, Duffy MJ, Andreasen PA: Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in human breast carcinomas. Int J Cancer 50: 208–214, 1992
Schmitt M, Jänicke F, Hafter R, Hollrieder A, Kanayama N, Gulba D, Graeff D (ed): Tumor-associated fibrinolysis in human breast cancer: detection and quantitation of the urokinase-type plasminogen activator (uPA) by ELISA and immunohistochemistry. Amsterdam: Elsevier Science Publishers BY, 1990: 213–222. Matsuda M, Iwanaga S, Takada A, Henschen A (ed) Fibrinogen 4: Current basic and clinical aspects
Sumiyoshi K, Serizawa K, Urano T, Takada Y, Takada A, Baba S: Plasminogen activator system in human breast cancer. Int J Cancer 50: 345–348, 1992
Clayman G, Wang SW, Nicolson GL, El-Naggar A, Mazar A, Henkin J, Blasi F, Goepfert H, Boyd DD: Regulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression in squamous-cell carcinoma of the oral cavity. Int J Cancer 54: 73–80, 1993
Boyd D, Ziober B, Chakrabarty S, Brattain M: Examination of urokinase protein/transcript levels and their relationship with laminin degradation in cultured colon carcinoma. Cancer Res 49: 816–820, 1989
de Bruin PA, Griffioen G, Verspaget HW, Verheijen JH, Dooijewaard G, van den Ingh HF, Lamers CB: Plasminogen activator profiles in neoplastic tissues of the human colon. Cancer Res 48: 4520–4524, 1988
Sier CF, Fellbaum C, Verspaget HW, Schmitt M, Griffioen G, Graeff H, Hôfler H, Lamers CB: Immunolocalization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in adenomas and carcinomas of the colorectum. Histopathology 19: 231–237, 1991
Kwaan HC: The plasminogen-plasmin system in malignancy. Cancer Metastasis Rev 11: 291–311, 1992
Hearing VJ, Law LW, Corti A, Appella E, Blasi F: Modulation of metastatic potential by cell surface urokinase of murine melanoma cells. Cancer Res 48: 1270–1278, 1988
Kirchheimer JC, Wojta J, Christ G, Binder BR: Functional inhibition of endogenously produced urokinase decreases cell proliferation in a human melanoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 5424–5428, 1989
Mignatti P, Robbins E, Rifkin DB: Tumor invasion through the human amniotic membrane: requirement for a proteinase cascade. Cell 47: 487–498, 1986
Ossowski LL:In vivo Invasion of modified chorioallantoic membrane by tumor cells: the role of cell surface-bound urokinase. J Cell Biol 107: 2437–2445, 1988
Ossowski L, Reich E: Antibodies to plasminogen activator inhibit human tumor metastasis. Cell 35: 611–619, 1983
Weidner N: The relationship of tumor angiogenesis and metastasis with emphasis on invasive breast carcinoma. In: Weinstein RL (ed) Advances in Pathology and Laboratory Medicine. 101–122. Chicago, IL: Mosby Year Book, Vol 5, 1992
Bacharach E, Itin A, Keshet E:In vivo patterns of expression of urokinase and its inhibitor PAI-1 suggest a concerted role in upregulating physiological angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89: 10686–10690, 1992
Burtin P, Chavanel G, André-Bougaran J, Gentile A: The plasmin system in human adenocarcinomas and their metastases. A comparative immunofluorescence study. Int J Cancer 39: 170–178, 1987
Kohga S, Harvey SR, Weaver RM, Markus G: Localization of plasminogen activators in human colon cancer by immunoperoxidase staining. Cancer Res 45: 1787–1796, 1985
Markus G, Camiolo SM, Kohga S, Madeja JM, Mittelman A: Plasminogen activator secretion of human tumors in short-term organ culture, including a comparison of primary and metastatic colon tumors. Cancer Res 43: 5517–5525, 1983
Sappino A-P, Belin D, Huarte J, Hirschel-Scholz S, Saurat JH, Vassalli JD: Differential protease expression by cutaneous squamous and basal cell carcinomas. J Clin Invest 88: 1073–1079, 1991
Skriver L, Larsson LI, Kielberg V, Nielsen LS, Andresen PB, Kristensen P, Danø K: Immunocytochemical localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in Lewis lung carcinoma. J Cell Biol 99: 752–757, 1984
Grøndahl-Hansen J, Ralfkiaer E, Kirkeby LT, Kristensen O, Lund LR, Danø K: Localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in stromal cells in adenocarcinomas of the colon in humans. Am J Pathol 138: 111–117, 1991
Pyke C, Kristensen P, Ralfiaer E, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Eriksen J, Blasi F, Danø K: Urokinase-type plasminogen activator is expressed in stromal cells and its receptor in cancer cells at invasive foci in human colon adenocarcinomas. Am J Pathol 138: 1059–1067, 1991
Danø K, Dabelsteen E, Nielsen LS, Kaltoft K, Wilson EL, Zeuthen J: Plasminogen activating enzyme in cultured glioblastoma cells. An immunofluorescence study with monoclonal antibody. J Histochem Cytochem 30: 1165–1170, 1982
Gross JL, Behrens DL, Mullins DE, Kornblith PL, Dexter DL: Plasminogen activator and inhibitor activity in human glioma cells and modulation by sodium butyrate. Cancer Res 48: 291–296, 1988
Helseth E, Dalen A, Unsgaard G, Vik R: Type beta transforming growth factor and epidermal growth factor suppress the plasminogen activator activity in a human glioblastoma cell line. J Neuro-Oncol 6: 277–283, 1988
Murphy P, Hart DA: Modulation of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor expression in the human U373 glioblastoma/astrocytoma cell line by inflammatory mediators. Exp Cell Res 198: 93–100, 1992
Nielsen LS, Hansen JG, Skriver L, Wilson EL, Kaltoft K, Zeuthen D, Danø K: Purification of zymogen to plasminogen activator from human glioblastoma cells by affinity chromatography with monoclonal antibody. Biochem 21: 6410–6415, 1982
Presta M, Ennas MG, Torelli S, Ragnotti G, Gremo F: Synthesis of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and type-1 plasminogen activator inhibitor in neuronal cultures of human fetal brain: stimulation by phorbol ester. J Neurochem 55: 1647–1654, 1990
Sitrin RG, Gyetko MP, Kole KL, McKeever P, Varani J: Expression of heterogeneous profiles of plasminogen activators and plasminogen activator inhibitors by human glioma lines. Cancer Res 50: 4957–4961, 1990
Landau BJ, Kwaan HC, Verrusio EN, Brem SS: Elevated levels of urokinase-type plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 in malignant brain tumors. Cancer Res 54: 1105–1108, 1994
Stoppelli MP, Corti A, Soffientini A, Cassani G, Blasi F, Assoian RK: Differentiation-enhanced binding of the amino-terminal fragment of human urokinase plasminogen activator to a specific receptor on U937 monocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82: 4939–4943, 1985
Vassalli JD, Baccino D, Belin D: A cellular binding site for the 55,000 form of the human plasminogen activator, urokinase. J Cell Biol 100: 86–92, 1985
Busso N, Belin D, Failly-Crépin C, Vassalli J-D: Plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in a human mammary cell line (HBL-100). Modulation by glucocorticoids. J Biol Chem 261: 9309–9315, 1986
Medcalf RL, Richards RI, Crawford RJ, Hamilton J: Suppression of urokinase-type plasminogen activator mRNA levels in human fibrosarcoma cells and synovial fibroblasts by anti-inflammatory glucocorticoids. EMBO J 5: 2217–2222, 1986
Emeis JJ, van Hinsberg VW, Verheijen JH, Wijngaards G: Inhibition of tissue-type plasminogen activator by conditioned medium from cultured human and porcine vascular endothelial cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 110: 392–398, 1983
Levin EG: Latent tissue plasminogen activator produced by human endothelial cells in culture: evidence for an enzyme-inhibitor complex. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 6804–6808, 1983
Loskutoff DJ, van Mourik JA, Erickson LA, Lawrence D: Detection of an unusually stable fibrinolytic inhibitor produced by bovine endothelial cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80: 2956–2960, 1983
Gelehrter TD, Barouski-Miller PA, Coleman PL, Cwikel BJ: Hormonal regulation of plasminogen activator in rat hepatoma cells. Mol Cell Biochem 53/54: 11–21, 1983
Laiho M, Saksela O, Andreasen PA, Keski-Oja J: Enhanced production and extracellular deposition of the endothelial-type plasminogen activator inhibitor in cultured human lung fibroblasts by transforming growth factor-beta. J Cell Biol 103: 2403–2410, 1986
Kobayashi H, Moniwa N, Gotoh J, Sugimura M, Terao T: Role of activated protein C in facilitating basement membrane invasion by tumor cells. Cancer Res 54: 261–267, 1994
Jänicke F, Schmitt M, Graeff H: Clinical relevance of the urokinase-type and tissue-type plasminogen activators and their type 1 inhibitor in breast cancer. Semin Thromb Hemost 17: 303–312, 1991
Pedersen H, Grøndahl-Hansen J, Francis D, Østerlind K, Hansen HH, Danø K, Brunner N: Urokinase and plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res 54: 120–123, 1994
Kristensen P, Pyke C, Lund LR, Andreasen PA, Danø K: Plasminogen activator inhibitor-type 1 in Lewis lung carcinoma. Histochemistry 93: 559–566, 1990
Shirasuna K, Saka M, Hayashido Y, Yoshioka H, Sugiura T, Matsuya T: Extracellular matrix production and degradation by adenoid cystic carcinoma cells: participation of plasminogen activator and its inhibitor in matrix degradation. Cancer Res 53: 147–152, 1993
Pyke C, Kristensen P, Ralfkiaer E, Eriksen J, Danø K: The plasminogen activation system in human colon cancer: messenger RNA for the inhibitor PAI-1 is located in endothelial cells in the tumor stroma. Cancer Res 51: 4067–4071, 1991
Cubellis MV, Wun T-C, Blasi F: Receptor-mediated internalization and degradation of urokinase is caused by its specific inhibitor PAI-1. EMBO J 9: 1079–1085, 1990
Herz J, Clouthier DE, Hammer RE: LDL receptor-related protein internalizes and degrades uPA-PAI-1 complexes and is essential for embryo implantation. Cell 71: 411–421, 1992
Olson D, Pöllänen J, Høyer-Hansen G, Rønne E, Sakaguchi K, Wun TC, Appella E, Danø K, Blasi F: Internalization of the urokinase: plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 complex is mediated by the urokinase receptor. J Bio Chem 267: 9129–9133, 1992
Schleef RR, Higgins DL, Pillemer E, Levitt LJ: Bleeding diathesis due to decreased functional activity of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Clin Invest 83: 1747–1752, 1989
Aillaud MF, Juhan-Vague I, Alessi MC, Marecal M, Vinson MF, Arnaud C, Vague P, Collen D: Increased PA-inhibitor levels in the postoperative period: no cause-effect relation with increased cortisol. Thromb Haemost 54: 466–468, 1985
Almér LO, Ohlin H: Elevated levels of rapid inhibitor of plasminogen activator (t-PAI) in acute myocardial infarction. Thromb Res 47: 335–339, 1987
Colucci M, Paramo JA, Collen D: Generation in plasma of a fast-acting inhibitor of plasminogen activator in response to endotoxin stimulation. J Clin Invest 75: 818–824, 1985
Páramo JA, Alfaro MJ, Rocha E: Postoperative changes in the plasmatic levels of tissue-type plasminogen activator and its fast-acting inhibitor-relationship to deep vein thrombosis and influence of prophylaxis. Thromb Haemost 54: 713–716, 1985
Sawaya R, Glas-Greenwalt P: Postoperative venous thromboembolism and brain tumors: part II. Hemostatic profile. J Neuro-Oncology 14: 127–134, 1992
Keeton M, Eguchi Y, Sawdey M, Ahn C, Loskutoff DJ: Cellular localization of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor messenger RNA and protein in murine renal tissue. Am J Pathol 142: 59–70, 1993
Keohane ME, Hall SW, VandenBerg SR, Gonias SL: Secretion of α2-macroglobulin, α2-antiplasmin, and plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 by glioblastoma multiforme in primary organ culture. J Neurosurg 73: 234–241, 1990
Murphy PG, Hart DA: Regulation of plasminogen activator and plasminogen activator inhibitor expression by cells of neural origin. Semin Thromb Hemost 17: 268–275, 1991
Rehemtulla A, Murphy P, Dobson M, Hart DA: Purification and partial characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor from the human glioblastoma, U138. Biochem Cell Biol 66: 1270–1277, 1988
Wagner SL, Lau AL, Nguyen A, Mimuro J, Loskutoff DJ, Isackson PJ, Cunningham DD: Inhibitors of urokinase and thrombin in cultured neuronal cells. J Neurochem 56: 234–242, 1991
Rao JS, Rayford A, Morantz RA, Festoff BW, Sawaya R: Increased levels of plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 (PAI-1) in human brain tumors. J Neuro-Oncology 17: 215–221, 1994
Kono S, Rao JS, Bruner JM, Sawaya R: Immunohistochemical localization of plasminogen activator inhibitor type 1 in human brain tumors. J Neuropath Exp Neurology 53: 256–262, 1994
Owensby DA, Morton PA, Wun T-C, Schwartz AL: Binding of plasminogen activator inhibitor type-1 to extracellular matrix of Hep G2 cells. Evidence that the binding protein is vitronectin. J Biol Chem 266: 4334–4340, 1991
Schneiderman J, Sawdey M, Craig H, Thinnes T, Bordin G, Loskutoff DJ: Type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression following partial hepatectomy. Am J Pathol 143: 753–762, 1993
Sprengers ED, Kluft C: Plasminogen activator inhibitor. Blood 69: 381–387, 1987
D'Amore PA, Thompson RW: Mechanisms of angiogenesis. Annu Rev Physiol 49: 453–464, 1987
Keski-Oja J, Koli K, Lohi J, Laiho M: Growth factors in the regulation of plasminogen-plasmin system in tumor cells. Semin Thromb Hemost 17: 231–239, 1991
Sawdey M, Podor TJ, Loskutoff DJ: Regulation of type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor gene expression in cultured bovine aortic endothelial cells: induction by transforming growth factor-β, lipopolysaccharide, and tumor necrosis factor-α. J Biol Chem 264: 10396–10401, 1989
Schleef RR, Bevilacqua MP, Sawdey M, Gimbrone MAJ, Loskutoff DJ: Cytokine activation of vascular endothelium. Effects on tissue-type plasminogen activator and type 1 plasminogen activator inhibitor. J Biol Chem 263: 5797–5803, 1988
Henderson BR, Tansey WP, Phillips SM, Ramshaw IA, Kefford RF: Transcriptional and posttranscriptional activation of urokinase plasminogen activator gene expression in metastatic tumor cells. Cancer Res 52: 2489–2496, 1992
Frixen UH, Nagamine Y: Stimulation of urokinase-type plasminogen activator expression by blockage of E-cadherin-dependent cell-cell adhesion. Cancer Res 53: 3618–3623, 1993
Saksela O, Moscatelli D, Rifkin DB: The opposing effects of basic fibroblast growth factor and transforming growth factor beta on the regulation of plasminogen activator activity in capillary endothelial cells. J Cell Biol 105: 957–963, 1987
Mignatti P, Tsuboi R, Robbins E, Rifkin DB:In vitro angiogenesis on the human amniotic membrane: requirement for basic fibroblast growth factor-induced proteinases. J Cell Biol 108: 671–682, 1989
Ciambrone GJ, McKeown-Longo PJ: Vitronectin regulates the synthesis and localization of urokinase-type plasminogen activator in HT-1080 cells. J Biol Chem 267: 13617–13622, 1992
Kost C, Stüber W, Ehrlich HJ, Pannekoek H, Preissner KT: Mapping of binding sites for heparin, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and plasminogen to vitronectin's heparin-binding region reveals a novel vitronectin-dependent feedback mechanism for the control of plasmin formation. J Biol Chem 267: 12098–12105, 1992
Christensen U, Holmberg L, Bladh B, Åstedt B: Kinetics of the reaction between urokinase and an inhibitor of fibrinolysis from placental tissue. Thromb Haemost 48: 24–26, 1982
Kruithoff EK, Vassalli JD, Schleuning WD, Mattaliano RJ, Bachmann F: Purification and characterization of a plasminogen activator inhibitor from the histocytic lymphoma cell line U-937. J Biol Chem 261: 11207–11213, 1986
Åstedt B, Lecander I, Brodin T, Lundblad A, Low K: Purification of a specific placental plasminogen activator inhibitor by monoclonal antibody and its complex formation with plasminogen activator. Thromb Haemost 53: 122–125, 1985
Hekman CM, Loskutoff DJ: Endothelial cells produce a latent inhibitor of plasminogen activators that can be activated by denaturants. J Biol Chem 260: 11581–11587, 1985
Estreicher A, Mühlhauser J, Carpentier JL, Orci L, Vassalli JD: The receptor for urokinase type plasminogen activator polarizes expression of the protease to the leading edge of migrating monocytes and promotes degradation of enzyme inhibitor complexes. J Cell Biol 111: 783–792, 1990
Foucré D, Bouchet C, Hacène K, Pourreau-Schneider N, Gentile A, Martin PM, Desplaces A, Oglobine J: Relationship between cathepsin B, urokinase, and plasminogen activator inhibitors in malignantvs benign breast tumors. Br J Cancer 64: 926–932, 1991
Sier CF, Verspaget HW, Griffioen C, Verheijen JH, Quax PH, Dooijewaard G, de Bruin PA, Lamers CB: Imbalance of plasminogen activators and their inhibitors in human colorectal carcinogenesis. Gastroenterology 101: 1522–1528, 1991
Nakamura M, Konno H, Tanaka T, Maruo Y, Nishino N, Aoki K, Baba S, Sakaguchi S, Takada Y, Takada A: Possible role of plasminogen activator inhibitor 2 in the prevention of the metastasis of gastric cancer tissues. Thromb Res 65: 709–719, 1992
Pujade-Lauraine E, Lu H, Mirshahi S, Soria J, Soria C, Bernadou A, Kruithof EKO, Lijnen HR, Burtin P: The plasminogen-activation system in ovarian tumors. Int J Cancer 55: 27–31, 1993
Cohen RL, Niclas L, Lee WMF, Wun T-C, Crowley CW, Levinson AD, Sadler JE, Shuman MA: Effect of cellular transformation on expression of plasminogen activator inhibitors 1 and 2: evidence for independent regulation. J Biol Chem 264: 8375–8383, 1989
Belin D, Wohlwend A, Schleuning WD, Kruithof EK, Vassalli J-D: Facultative polypeptide translocation allows a single mRNA to encode the secreted and cytosolic forms of plasminogen activators inhibitor-2. EMBO J 8: 3287–3294, 1989
Baker JB, Low DA, Simmer RL, Cunningham DD: Protease-nexin: a cellular compornent that links thrombin and plasminogen activator and mediates their binding to cells. Cell 21: 37–45, 1980
McGrogan M, Kennedy J, Li MP, Hsu C, Scott RW, Simonsen C, Baker JB: Molecular cloning and expression of two forms of human protease nexin I. Biotechnology 6: 172–177, 1988
Scott RW, Baker JB: Purification of human protease nexin. J Biol Chem 258: 10439–10444, 1983
Gloor S, Odink K, Guenther J, Nick H, Monard D: A glia-derived neurite promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity belongs to the protease nexins. Cell 47: 687–693, 1986
Guenther J, Nick H, Monard D: A glia-derived neurite-promoting factor with protease inhibitory activity. EMBO J 4: 1963–1966, 1985
Wagner SL, Geddes JW, Cotman CW, Lau AL, Gurwitz D, Isackson PJ, Cunningham DD: Protease nexin-1, an antithrombin with neurite outgrowth activity, is reduced in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86: 8284–8288, 1989
Rosenblatt DE, Cotman CW, Nieto-Sampedro M, Rowe JW, Knauer DJ: Identification of a protease inhibitor produced by astrocytes that is structurally and functionally homologous to human protease nexin-I. Brain Res 415: 40–48, 1987
Monard D: Cell-derived proteases and protease inhibitors as regulators of neurite outgrowth. Trends Neurosci 11: 541–544, 1988
Vaughan PJ, Cunningham DD: Regulation of protease nexin-1 synthesis and secretion in cultured brain cells by injury-related factors. J Biol Chem 268: 3720–3727, 1993
Cavanaugh KP, Gurwitz D, Cunningham DD, Bradshaw RA: Reciprocal modulation of astrocytes stellation by thrombin and protease nexin-1. J Neurochem 54: 1735–1743, 1990
Rao JS, Baker JB, Morantz RA, Kimler B, Evans R, Festoff BW: Serpin inhibitors of urokinase and thrombin in normal rat brain and 9L brain tumor: evidence for elevated expression of protease nexin 1-like inhibitor and a novel sodium dodecyl sulfate-activated tumor antithrombin. Cancer Res 50: 5039–5044, 1990
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yamamoto, M., Sawaya, R., Mohanam, S. et al. Activities, localizations, and roles of serine proteases and their inhibitors in human brain tumor progression. J Neuro-Oncol 22, 139–151 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052889
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01052889